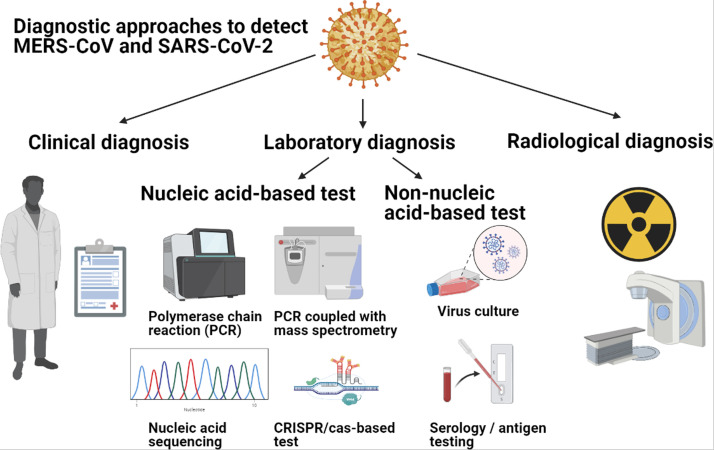
Fig. 1.
Various diagnostic approaches which could be used to detect MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV infections. Clinical diagnosis relies on history taking and clinical assessment to determine whether an individual is at high risk of contracting the coronaviruses [6], [29], [30], [33]. Laboratory diagnostic tests can be divided into nucleic acid-based, protein-based, and virus-culture tests [16], [17]. Examples of nucleic acid-based diagnostic tests include polymerase chain reactions like qRT-PCR and dPCR, or RT-LAMP, RT-RPA, PCR-coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) and CRISPR/Cas-based detection test [16], [17], [99], [104], [105], [118], [121], [126], [185], [54], [57], [66], [74], [77], [95], [96], [97]. Protein-based diagnostic tests include virus serology, neutralization and virus antigen tests [2], [16], [17], [54], [57], [126], [180], [185], [257]. Radiological diagnosis involves the use of chest radiography or CT scan to assess the thoracic cavity of the individuals who are suspected to have pneumonia secondary to coronavirus infection [16], [277], [278], [279].