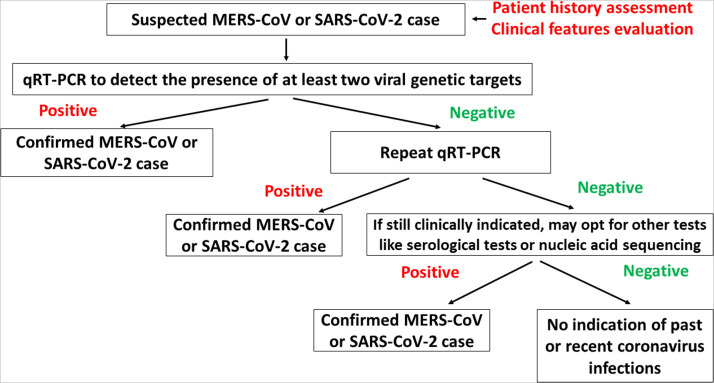
Fig. 2.
Diagnostic approaches to confirm the presence of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. For clinically suspicious cases, qRT-PCR remains as the gold standard molecular diagnostic test to confirm MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV infections [6], [29], [30], [33], [34], [57], [126]. For individuals who have negative qRT-PCR test results, a repeat test is highly recommended [29], [34], [54], [57]. In the case in which qRT-PCR results are inconclusive, further tests like nucleic acid sequencing and serological tests could be performed to confirm the coronavirus infection [29], [34], [54], [57]. For MERS-CoV, the guidelines state that the patients need to have at least two consecutive negative qRT-PCR results before they are allowed to be discharged from the isolation services [29], [54]. However, for SARS-CoV-2, the latest guideline recommends that the symptomatic patient is allowed to be discharged 10 days after the onset of symptoms while asymptomatic patients could be discharged 10 days after the molecular diagnosis of the virus. [58].