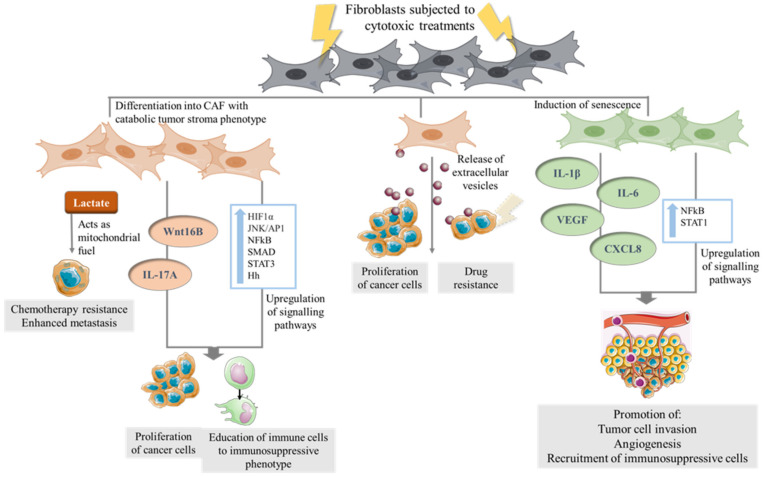
Figure 2.
The direct effect of cytotoxic therapies on CAF. Fibroblasts in the TME of cancer cells which are subjected to cytotoxic therapies undergo transformation to a catabolic tumor stroma phenotype secreting metabolites such as lactate which in turn serves as mitochondrial fuel for cancer cells. Chemotherapy can stimulate stress-linked signaling pathways in CAF and the secretion cytokines lead to a microenvironment which in turn can promote cancer proliferation and educate immune cells to an immunosuppressive phenotype. Senescence induction in CAF have been shown to upregulate signaling pathways, leading to secretion of cytokines which promote tumor cell invasion, angiogenesis and the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). CAF exposed to cytotoxic therapies release EVs which are taken up by cancer cells, leading to increased expression of genes associated with increased proliferation and drug resistance.