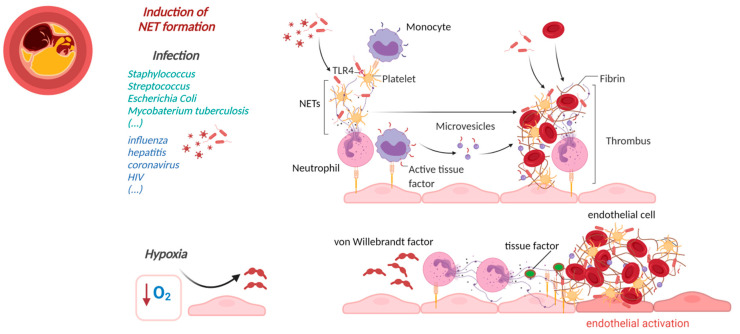
Figure 2.
NETs-initiated thrombosis. (Left): Cross section of a thrombus occluded artery. (Middle): NETs initiators; (Right): Pathogens may activate neutrophils to form neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) which support (immuno)thrombosis e.g., through histone-dependent platelet activation or binding to von Willebrand factor (VWF) and display of tissue factor within the NETs structure. (made with biorender.com, accessed on 4 June 2001).