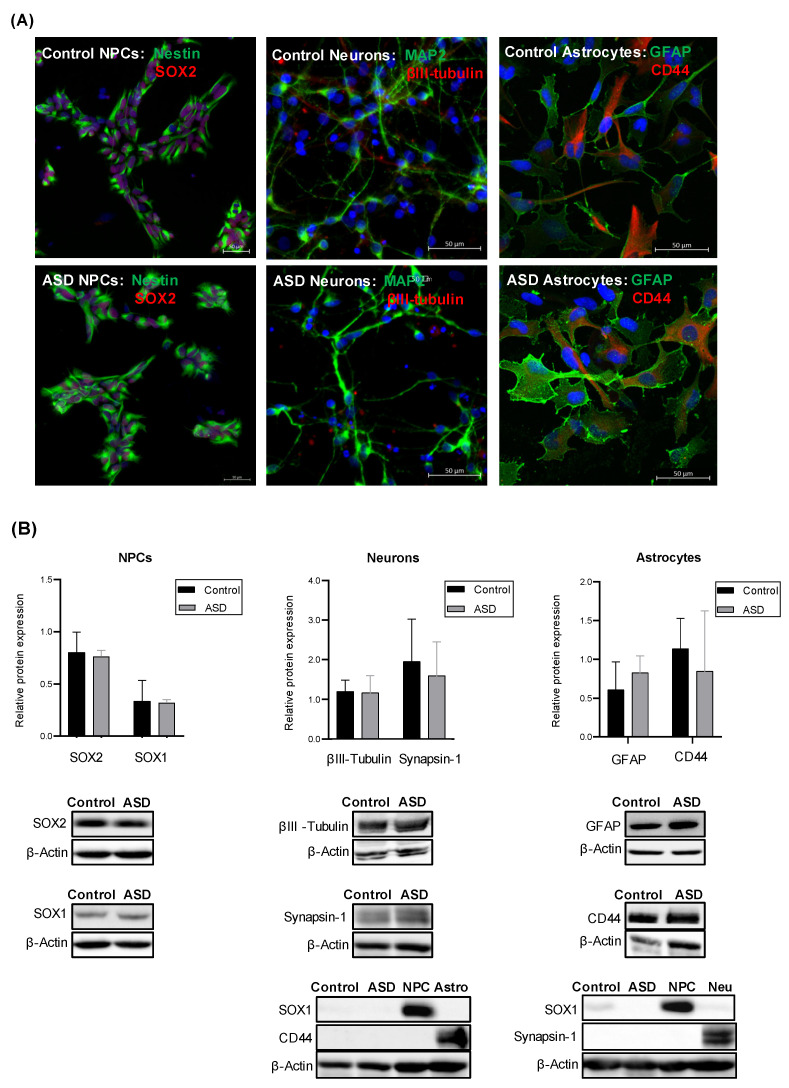
Figure 1.
Expression of lineage-specific markers in iPSC-derived NPCs, neurons and astrocytes. (A) Representative images of control- and ASD-derived: NPCs, showing the expression of the neural progenitor markers Nestin, an intermediate filament protein, and SOX2, a transcription factor that regulates pluripotency; neurons showing the expression of the neuron-specific cytoskeleton proteins MAP2 and βIII-tubulin; astrocytes showing the expression GFAP, one of the major intermediate filament protein of astrocytes, and CD44, a cell adhesion protein expressed by astrocyte precursor cells. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). All scale bars represent 50 μm. (B) Relative protein levels of: SOX2 and SOX1 in iPSC-derived NPCs of control (n = 4) and ASD (n = 7) subjects; βIII-tubulin and Synapsin-1, a synaptic vesicle-associated protein, in iPSC-derived neurons of control (n = 4) and ASD (n = 5) subjects; GFAP and CD44 in iPSC-derived astrocytes of control (n = 4) and ASD (n = 5) subjects. β-actin was used as a loading control. Representative immunoblot images of each lineage-specific marker are shown. No significant differences in the expression levels of these lineage markers were observed between the control and ASD groups. Furthermore, in order to verify whether the neuron cultures were contaminated by NPCs and astrocytes, as well as whether the astrocyte cultures were contaminated by NPCs and neurons, the expression of SOX1 and CD44 was measured in control- and ASD-derived neurons, and the expression of SOX1 and Synapsin-1 was measured in control- and ASD-derived astrocytes. NPC = iPSC-derived NPCs used as the control; Neuro = iPSC-derived neurons used as the control; Astro = iPSC-derived astrocytes used as the control. No detectable expression of SOX1 and CD44 was found in neurons, and no detectable expression of SOX1 and Synapsin-1 was found in astrocytes, suggesting that these cultures were not mixed neuronal/glial cultures.