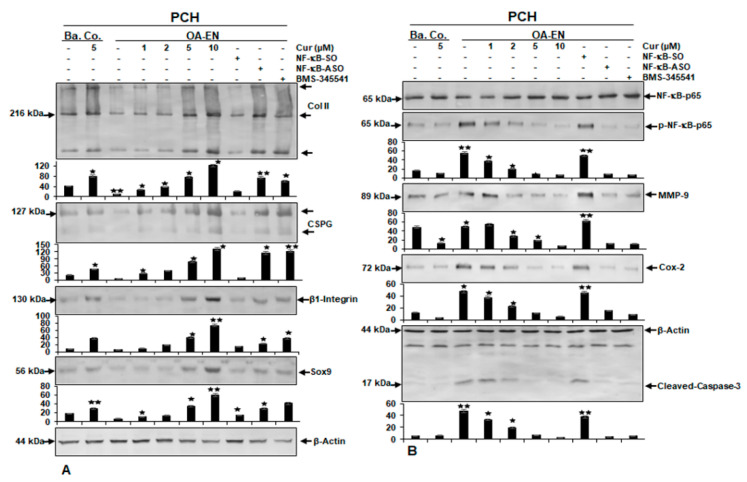
Figure 4.
Influence of curcumin, ASO against NF-kB, BMS-345541 upon extracellular matrix, β1-integrin, Sox9, NF-kB, NF-kB-promoted pro-inflammatory, matrix-degrading, and apoptotic proteins on chondrocytes in the osteoarthritic environment. Panel A-B: Serum-depleted chondrocytes (PCH) in alginate cultures by themselves (Ba. Co.) were kept nontreated or treated with curcumin (Cur), or co-cultured with fibroblasts and T-lymphocytes (OA-EN) and kept nontreated or treated with different doses of curcumin, or transfected with NF-kB-SO or NF-kB-ASO or treated with BMS-345541 for 14 days as outlined in Materials and Methods. Total cell samples were obtained, separated via SDS-PAGE, and subjected to western blot assay with antibodies against panel A: Collagen II, CSPG, β1-integrin, Sox9 panel B: NF-kB, phospho-NF-kB, MMP-9, Cox-2, and activated Caspase-3. β-Actin served as a loading control in each assay. Bars represent the mean values for each antibody along with standard variations of at least three separate experiments. Data were compared to the control. Statistically meaningful levels of p < 0.05 are marked with (★) and p < 0.01 with (★★).