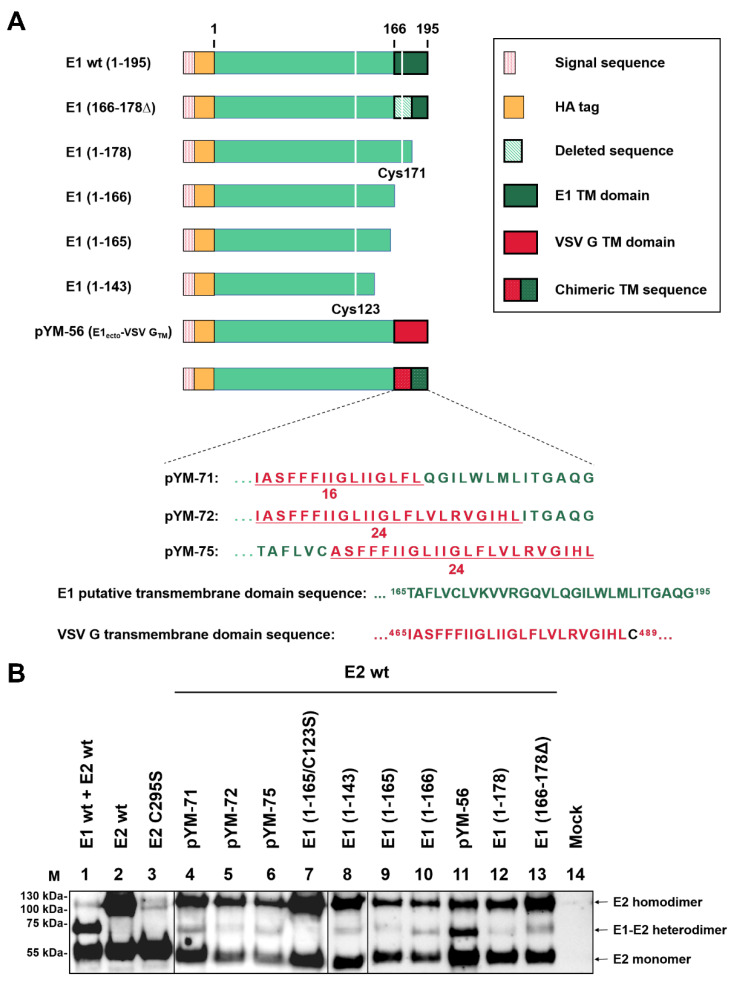
Figure 4.
Heterodimer formation analysis. (A) Schematic representation of the HA-E1 wild type and Carboxy-terminally truncated E1 constructs used in this section. Cysteine residues C123 and C171 are presented as white lines in the green bar representing the E1 sequence. Further constructs shown here encode HA-E1 with the TM domain or parts thereof replaced by sequences from the TMD of VSV. Below the schemes, the amino acid sequences of the chimeric TMDs are given in the one letter code (see also [23]). (B) The given Carboxy-terminally truncated E1 expression plasmids were co-transfected with a plasmid coding for E2 wt into RK-13 cells. Co-expression products were analyzed via nonreducing SDS-PAGE and Western blot using mAb α-E2 (WB214) for the detection of the E1/E2 heterodimer and E2 monomer/homodimer. A file is provided in the Supplementary Materials with the original Western blot results to demonstrate that the two parts were derived from equivalent gels and the mock control was run on one of these gels.