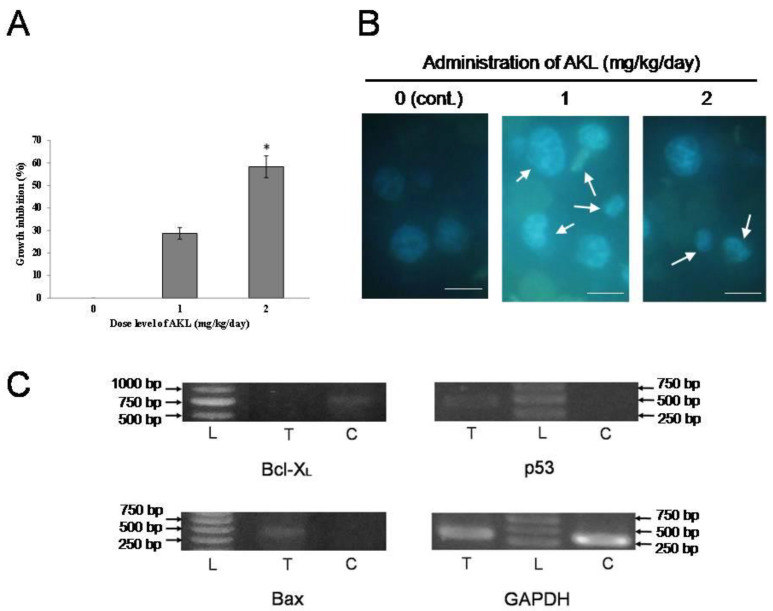
Figure 4.
In vivo anticancer activity of AKL-40. (A). Growth inhibition in AKL-40 treated mice compared to the untreated mice. The lectin was administrated to mice at doses 0 (untreated), 1 and 2 mg/kg/day (treated). Data are expressed in mean ± SD (n = 6). The results were statistically significant (* p < 0.05, when cells from lectin-treated mice were compared to cells from untreated mice). (B). Change of morphology in Hoechst-stained EAC cells harvested from AKL-40 treated mice. EAC cells from untreated and treated (with 1 mg/kg/day and 2 mg/kg/day of AKL-40, for five days) mice were observed by a fluorescence microscope. White arrows show changes in the morphology of cells. Scale bar: 25 µm. (C). Expression of apoptosis-related genes (Bcl-XL, p53 and Bax) and GAPDH. L, 1000 bp DNA ladder; T, RNA of EAC cells from AKL-40 treated mice; C, RNA of EAC cells from untreated (control) mice.