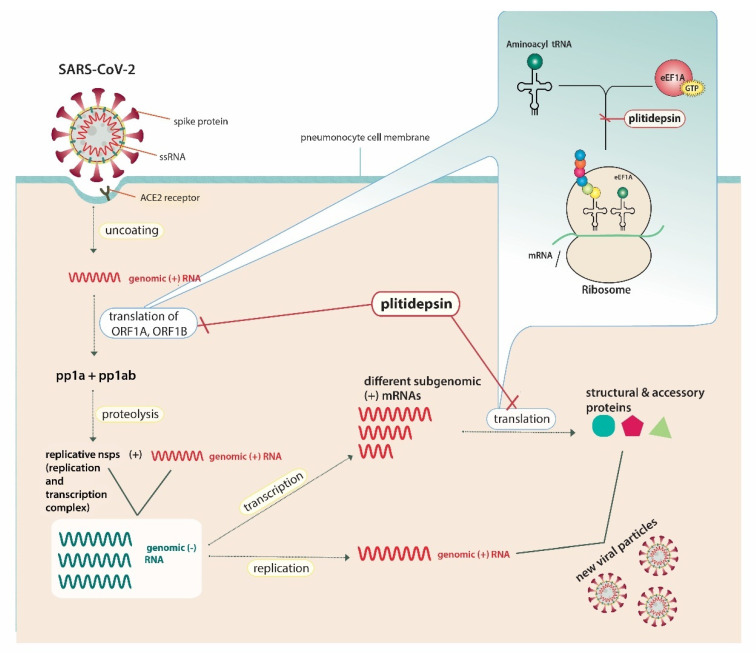
Figure 1.
Plitidepsin’s host-directed anti-SARS-CoV-2 action mechanisms.SARS-CoV-2 possesses a single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) genome. The angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) receptor is identified as the cell-surface receptor of SARS-CoV-2. Specific spike protein interactions with ACE2 receptors promote viral fusion with the cellular membrane. After entry, uncoating of the viral genomic RNA is followed by the translation of two large open reading frames (ORF), ORF1A and ORF1B. The resulting polyproteins, pp1a and pp1ab, are proteolyzed into non-structural proteins (nsps) that form the viral replication and transcription complex. This complex includes, amongst others, RNA-processing and RNA-modifying enzymes, such as RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase, and drives the production of negative-sense RNAs ((−) RNAs). In general, the positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins, whereas negative-sense RNA is converted (via RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase) into positive-sense RNA in order to be translated. Genomic RNA contains the necessary RNA regions required for genome replication and translation. During replication, full-length (−) RNA copies of the genome (genomic (−) RNAs) are used as templates for genomic (+) RNAs. During transcription, various subgenomic RNAs are produced through discontinuous transcription, where subgenomic (−) RNAs are synthesized by combining varying lengths of the 3′ end of the genome with the 5′ leader sequence necessary for translation. Subgenomic (−) RNAs are then transcribed into subgenomic (+) mRNAs. Resulting structural and accessory viral proteins are combined with genomic (+) RNAs to produce new viral particles, which will be secreted from the infected pneumonocyte by exocytosis. Through targeting the host cell’s eukaryotic translation elongation factor (eEF1A), plitidepsin inhibits the host-mediated translation of ORF1A, ORF1B and subgenomic mRNAs, leading to decreased production of viral pp1a and pp1ab andnsps, including RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase, as well as structural and accessory proteins. Abbreviations: SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; ACE2, angiotensin converting enzyme-2; ORF, open reading frame; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; tRNA, transfer ribonucleic acid; eEF1A, eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; pp, polyprotein.