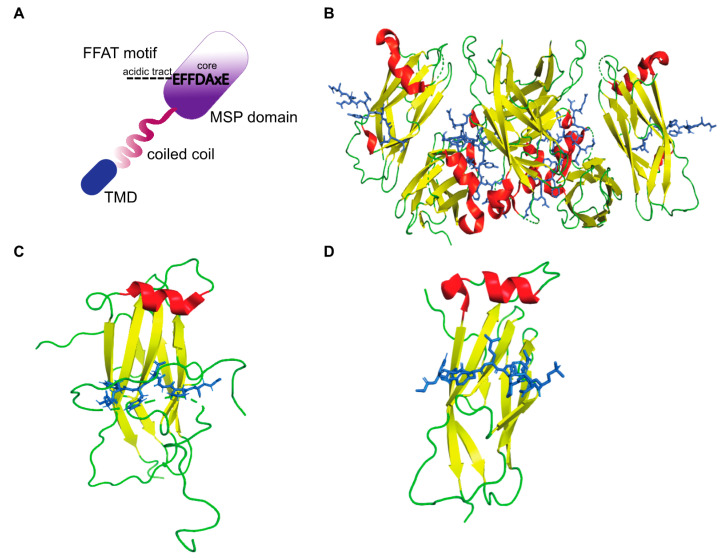
Figure 2.
The structure of VAP-FFAT complexes. (A) Schematic representation of a conventional FFAT motif binding the MSP domain of VAP. The electropositive surface of the MSP domain binds the core residues of the FFAT motif, and the dotted lines represent the acidic tract. (B) The crystal structure of rat MSP-VAPA in complex with the ORP1 FFAT motif as described by Kaiser et al. [19] (PDB ID: 1Z9O). A tetramer formed by MSP-FFAT complex is shown. (B–D) The MSP domain is represented as ribbons (red: helix, yellow: β-sheet, green: loop), and the FFAT motif is represented as sticks (blue) that bind across the MSP domain. (C) The crystal structure of human MSP-VAPA in complex with OSBP-FFAT as described by Furuita et al. [51] (PDB ID: 2RR3). (D) Structure of human-MSP-VAPA in complex with STARD3 FFAT as described by Di Mattia et al. [52] (PDB ID: 6TQR).