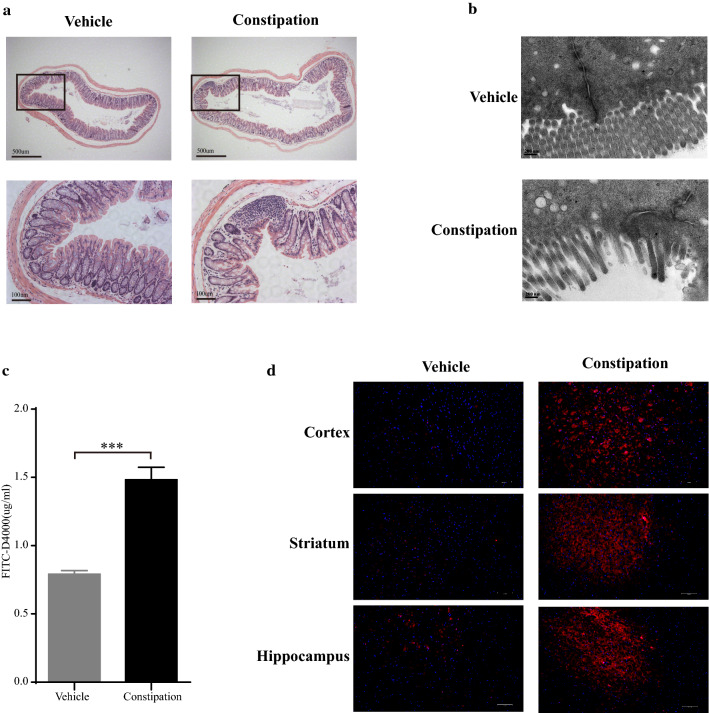
Fig. 2.
Constipation induced colon inflammation and injury, increased permeability of intestinal barrier and BBB in mice. After the constipation induction, distal colon was isolated and performed HE staining (× 50, scale bars = 500 μm; × 200, scale bars = 100 μm) (a) and TEM (× 42,000, scale bars = 200 nm) (b) for the pathological assessment. Mice were given FITC-D4000 at a dose of 600 mg/kg by oral gavage and the plasm was collected after 1 h to assess the intestinal permeability. The FITC-D4000 concentration in the plasm from different groups (c). Mice were intravenously injected with 0.4% EB at a dose of 200 mg/kg and circulated for 30 min. Cortex, striatum and hippocampus were obtained and tissue cryo-sections were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy for BBB permeability assessment (d). N = 6 in each group. Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001