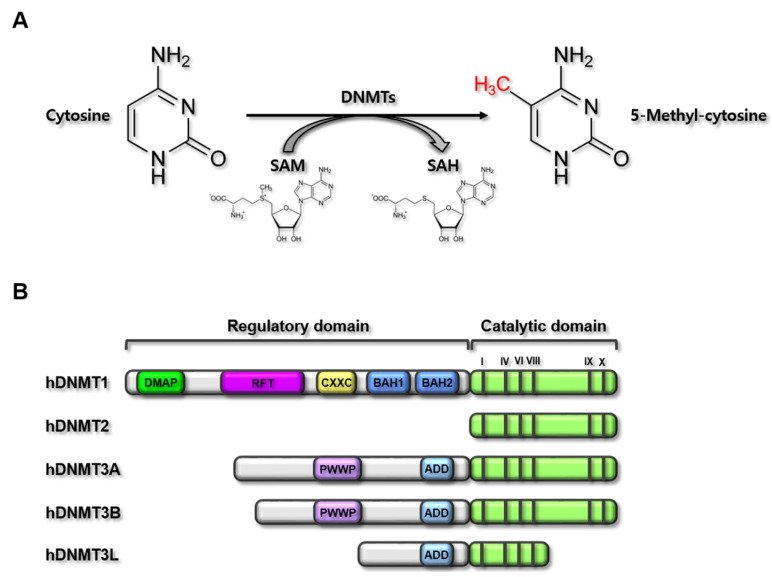
Figure 2.
DNMT-mediated methylation reaction and domain structure of human DNMTs. (A) Chemical reaction of DNMT-mediated methylation. DNMTs catalyze the methylation at cytosines of CpG in the gene promoter regions by transferring methyl groups from methyl donor, SAM, producing 5-methyl-cytosine in the gene promoter regions and SAH. (B) Domain structures of human DNMT (hDNMT) family members. hDNMTs consist of five members; hDNMT1 (1616 amino acids), hDNMT2 (391 amino acids), hDNMT3A (912 amino acids), hDNMT3B (853 amino acids), and hDNMT3L (386 amino acids). hDNMTs have two main domains; the regulatory and catalytic domains. The catalytic domain is conserved in all hDNMTs. hDNMT1 is the longest member with DMAP, RFTD, CXXC, and two BAHs in the regulatory domain. hDNMT2 is the smallest member existing only catalytic domain. hDNMT3A and hDNMT3B have PWWP and ADD in the regulatory domain in common, but hDNMT3B is little bit smaller than hDNMT3A. hDNMT3L has only ADD in the regulatory domain with the shorter catalytic domain. Bars in the catalytic domain (I, IV, VI, VIII, IX, and X) represent the catalytic active sites. SAM, S-adenosyl-l-methionine; SAH, S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; DMAP, DNA methyltransferase-associated protein 1-interacting domain; RFT, replication foci targeting sequence domain; CXXC, CXXC domain; BAH, bromo-adjacent homology domain; PWWP, PWWP domain; ADD, ATRX-DNMT3-DNMT3L domain.