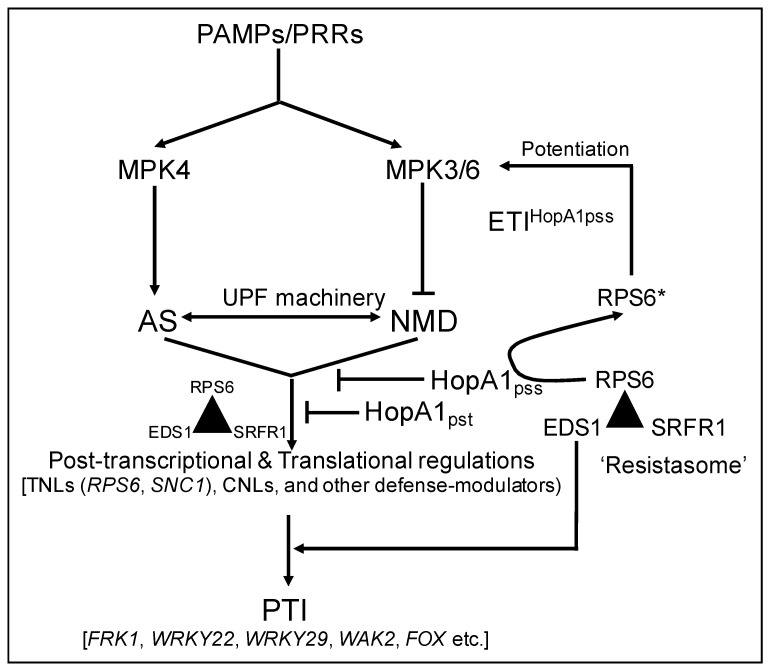
Figure 7.
Schematic hypothetical model of HopA1 virulence, elicitation of ETIHopA1pss and potentiation on PTI. PAMP perceptions by PRRs elicit PTI utilizing the MAPK (MPK3/4/6) networks to perturb AS-NMD pathway through the degradation of UPF proteins, phosphorylation of splicing and other associated factors. Upregulated splice variants of TNLs (RPS6, SNC1) and other defense-associated transcripts contribute to PTI signaling. Defensive overshoots are prevented by the macromolecular ‘resistasome complex (triangle) functions comprising of SRFR1, EDS1 and TNLs (RPS6). Protein-protein interactions with SRFR1 modulate uncontrolled activation of RPS6. In susceptible plants, HopA1s suppress PTI via post-transcriptional and translational inhibitions of immune-related transcripts (such as FRK1, WRKY22, WRKY29, WAK2, FOX) including TNLs. In resistant plant, resistasome sense HopA1pss activities to cause activation of RPS6 (RPS6*) through unknown mechanisms. The elicited ETIHopA1pss amplify PTI through MAPK3/6 signaling and other unidentified routes.