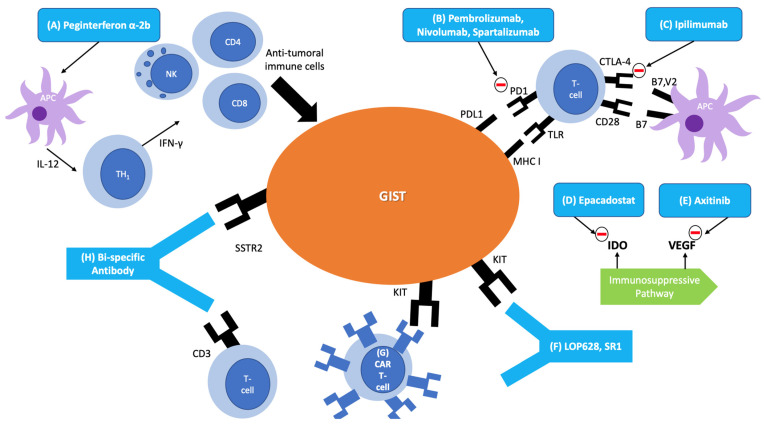
Figure 1.
Immunotherapies in GIST. (A) Cytokine Therapy: Peginterferon alpha-2b is a cytokine-based therapy that is used in combination with imatinib to treat stage III/IV GIST. It functions by presenting an antigen cocktail to an antigen presenting cell (APC) to induce an IL-12 mediated TH1 immune response. The TH1 response secretes interferon-gamma and activates anti-tumoral immune cells. (B–E) Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: (B) Pembrolizumab, Nivolumab, and Spartalizumab are programmed cell death protein-1 (PD1) inhibitors, preventing the PD1 and PDL1 interaction that leads to immune suppression and evasion of the immune system by cancer cells. (C) Ipilimumab is a CTLA-4 antibody, inhibiting the receptor’s function of sending inhibitory signals to T cells. (D) Epacodostat inhibits indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), an enzyme that decreases immune surveillance by downregulating NK and CD8 cells while upregulating T-regs. (E) Axitinib inhibits VEGF, thereby inhibiting the immunosuppressive function of VEGF. (F) Anti-KIT Antibodies: microtubule destabilizing maytansinoid (LOP628) and SR1 are monoclonal antibodies able to slow the growth of GIST via downregulation of KIT. (G) Cellular Therapy: Anti-KIT chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells bind to GIST tumor cells leading to cell lysis. (H) Bi-specific monoclonal antibodies: binds to a somatostatin receptor (SSTR2) on tumor cells and CD3 to trigger a potent cytotoxic T cell response.