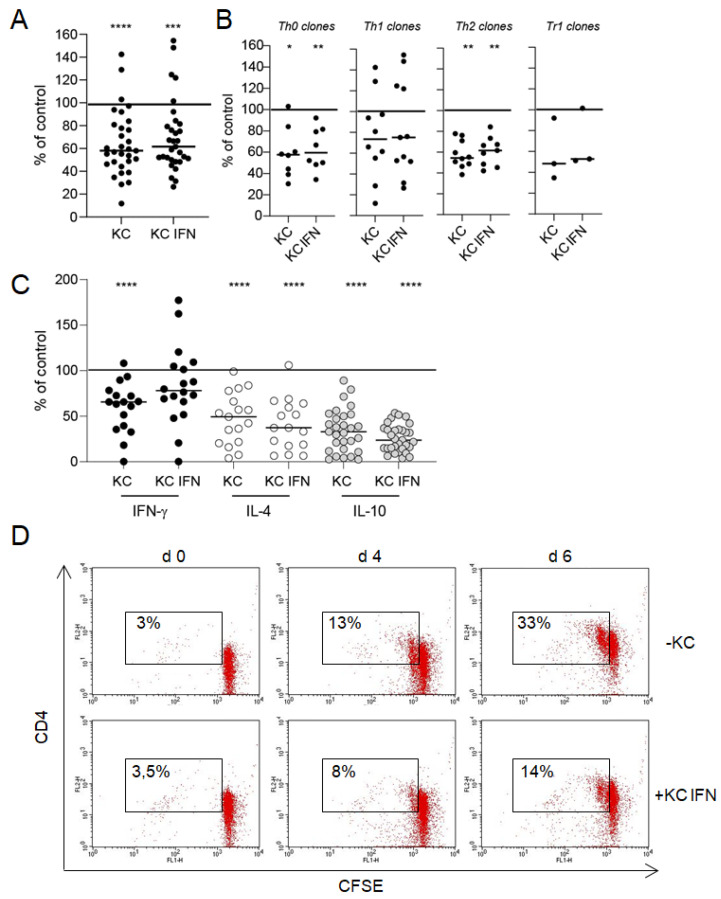
Figure 2.
Interaction between keratinocytes and T cells results in an inhibition of T cell effector functions. Keratinocytes (KC) or IFN-γ prestimulated keratinocytes (KC IFN), autologous nickel-specific T cell clones and DCs were incubated in a ratio of 10:100:1 in the presence of nickel sulfate. After 48 h, nickel-specific T cell proliferation was measured by 3H-thymidine incorporation (A,B), and the production of cytokines was detected in a cell-free co-culture supernatants by ELISA (C). Each data point represents one T cell clone with an average of at least three experiments (T cell clones pooled, panel (A); T cell clone subsets, panel (B)). The line displays the median of all clones investigated. Shown is the percentage change of T cell proliferation and cytokine production compared to the control culture without keratinocytes (normalized to 100%). The inhibitory effect of keratinocytes on T cell proliferation could also be observed in a flow cytometric approach with CFSE-labeled T cell clones (D). The number indicates the CD4+, proliferating T cells. ((A–C) clones = 32, n = 105, (D) one representative clone in co-culture with IFN-γ prestimulated keratinocytes; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ****: p < 0.0001).