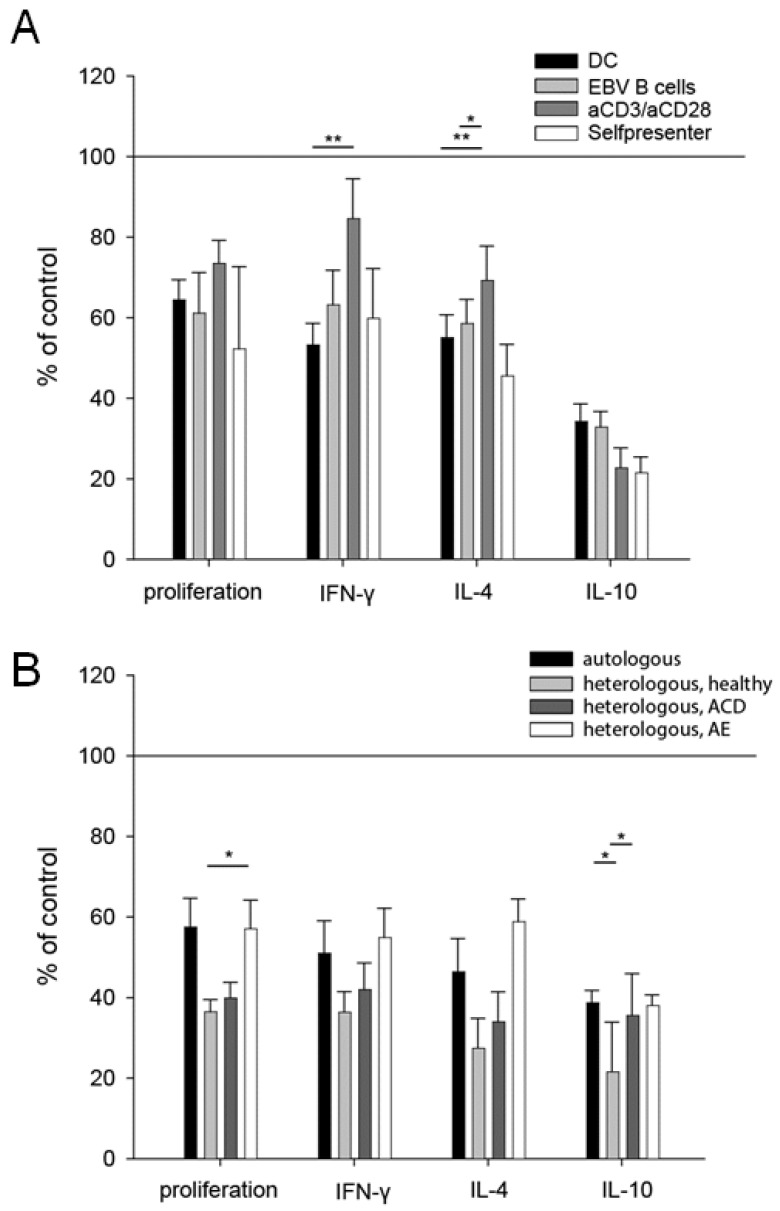
Figure 4.
The inhibitory capacity of keratinocytes is independent of the antigen presentation and HLA-TCR interactions. Nickel-specific T cell clones were co-cultured with autologous keratinocytes, nickel sulfate and different types of APCs (dendritic cells (DC), Epstein–Barr-virus-transfected B cells (EBV B cells)), TCR stimuli (anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibodies) or in the absence of professional APCs as self-presenter cells (self) (A). Comparison of the co-culture of nickel-specific T cells, DCs, nickel sulfate and autologous keratinocytes to the co-culture with heterologous keratinocytes (B). The heterologous keratinocytes were obtained from a healthy volunteer, a patient with ACD to nickel and one patient with atopic eczema/dermatitis (AE). All conditions showed significant differences, compared to the control condition (set to 100%) (p < 0.05). Results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey correction for multiple testing. ((A) DC clones = 13, n = 50; EBV clones 20, n = 53; aCD3/aCD28 clones 8, n = 25; self-presenter clones 8, n = 33; (B) autologous n = 35; heterologous healthy n = 10; heterologous ACD n = 22; heterologous AE n = 8); *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01).