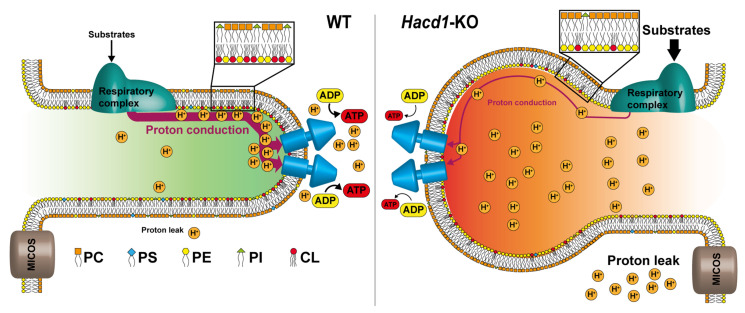
Figure 12.
A proposed model of the molecular mechanism underlying the mitochondrial uncoupling in HACD1-deficient muscles. In wild type conditions, anionic lipids included in the cristae lumen leaflet of the IMM contribute to the translocation of protons to the tip of the cristae, where ATP synthase oligomers concentrate. In Hacd1-KO mice, the decreased content of anionic lipids changes cristae shape, reduces efficiency of proton translocation, hence impairing ATP production.