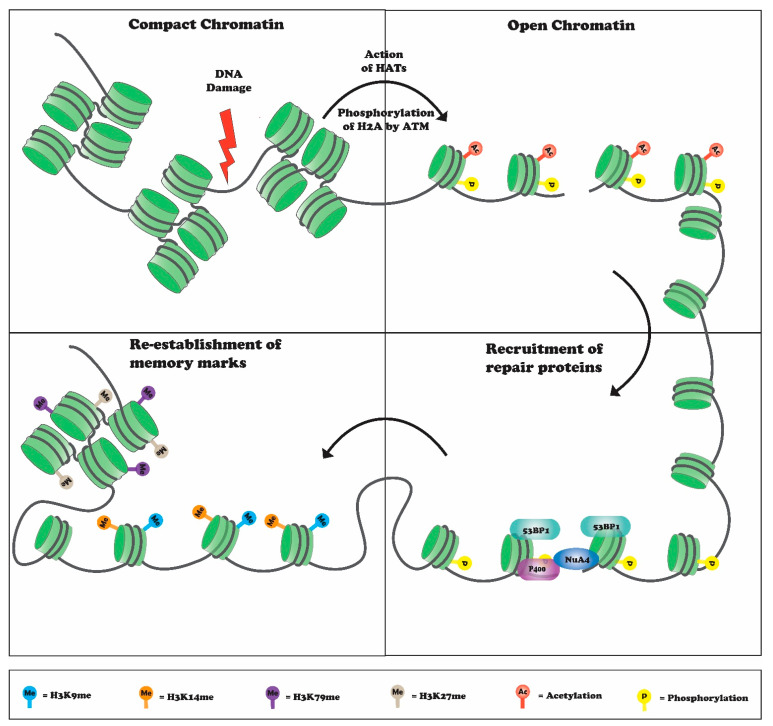
Figure 1.
DNA damage initiates chromatin decompaction mediated by various histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and recruits various DSB-repair and chromatin-modifying proteins. Binding of these proteins, such as 53BP1, NuA4, and P400, leads to DSB repair followed by chromatin compaction, which helps in maintaining genome integrity.