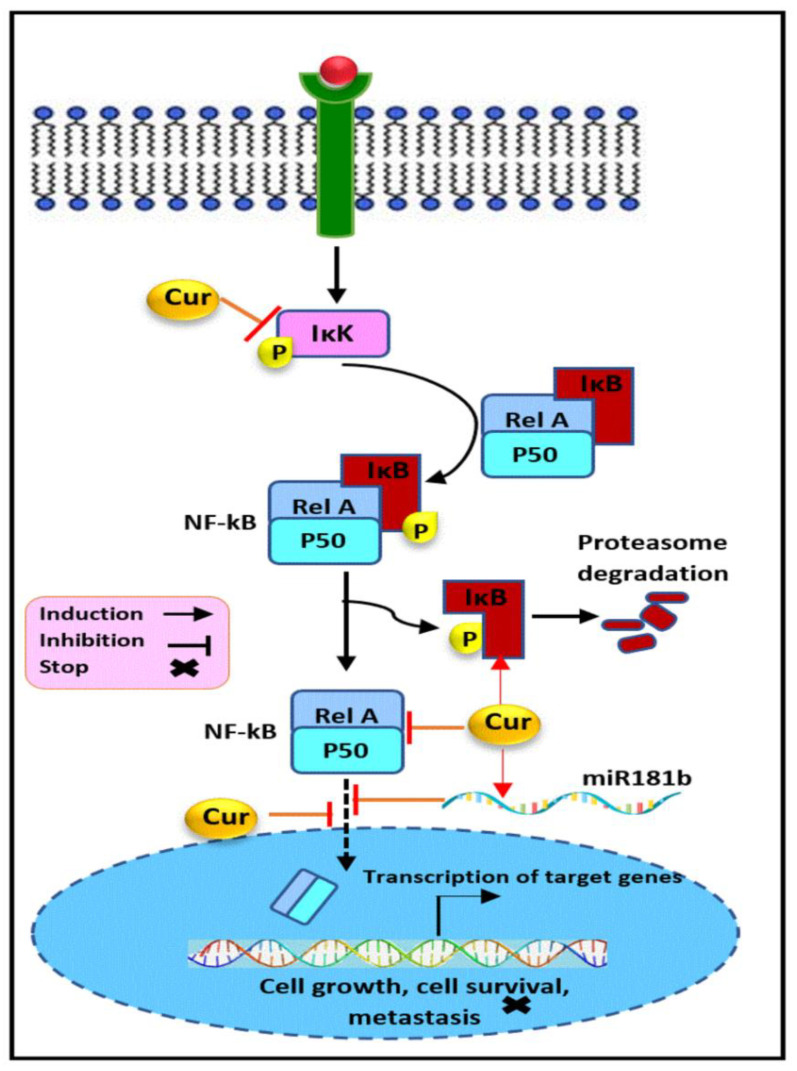
Figure 4.
The modulatory effect of curcumin on the NF-κB pathway. Curcumin inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway through the regulation of its key components. Curcumin upregulates IκB and miR181b expression and downregulates NF-κB and IKK, and suppresses the NF-κB translocation into the nucleus, which results in the inhibition of cellular proliferation, survival, metastasis, and angiogenesis in hormone receptor negative breast cancer. Cur: curcumin, IκK: inhibitor of kappa B kinase, IκB: inhibitor of NF-κB, Rel A: p65.