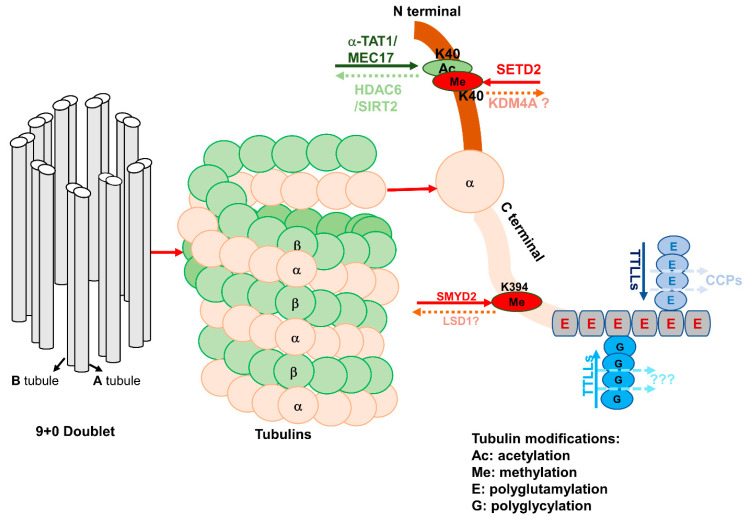
Figure 2.
Epigenetic-regulator-mediated tubulin post-translational modifications (PTMs). Left: Schematic drawings of an axoneme composed of 9 doublets (A tubule and B tubule) of microtubules in primary cilia. The microtubules are composed of heterodimers of α-tubulin and β-tubulin. Right: The PTMs of α-tubulin associated with the cell cycle and cilia biogenesis include acetylation, methylation, polyglutamylation, and polyglycylation. Lysine K40 of α-tubulin can be either acetylated by a-TAT1/MEC17 or methylated by SETD2, which can be deacetylated by HDAC6/SIRT2 and possibly demethylated by KDM4A. The acetylation of α-tubulins at K40 occurs on the luminal surface of the microtubules. SMYD2 methylates a-tubulin at K394, which may be demethylated by LSD1. (Poly)glycylation and (poly)glutamylation are found along the glutamate-rich carboxy-terminal tails of α-tubulin, which are regulated by different subsets of tubulin tyrosine ligase-like glutamylases (TTLLs). Ac: Acetylation; Me: methylation; E: polyglutamylation; G: polyglycylation.