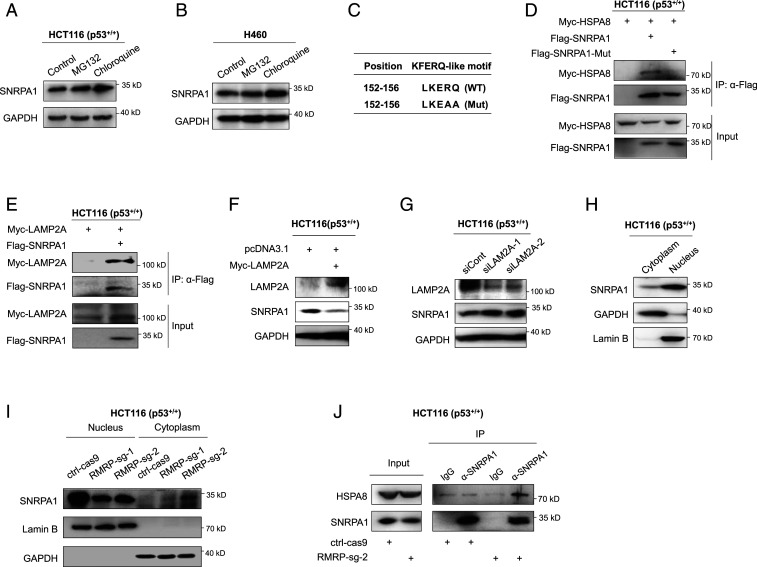
Fig. 6.
RMRP prevents lysosomal proteolysis of SNRPA1 by perturbing CMA. (A and B) SNRPA1 protein is stabilized by the autophagy inhibitor CQ but not by the proteasome inhibitor MG132. HCT116 p53+/+ (A) and H460 (B) cells were treated with MG132 (20 μM, 6 h) and CQ (50 μM, 8 h) before harvested for IB. (C) The presence of a KFERQ-like motif, LKERQ, in SNRPA1 and mutation of this motif to LKEAA. (D) Exogenous SNRPA1 interacts with exogenous HSPA8 via the LKERQ motif. HCT116 p53−/− cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding Myc-HSPA8, Flag-SNRPA1, and Flag-SNRPA1-Mut followed by co-IP–IB assays. (E) Exogenous SNRPA1 interacts with exogenous LAMP2A. HCT116 p53−/− cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Flag-SNRPA1 and Myc-LAMP2A followed by co-IP–IB assays. (F) Overexpression of LAMP2A reduces the protein level of SNRPA1 in HCT116 p53+/+ cells. (G) Knockdown of LAMP2A increases the expression of SNRPA1 in HCT116 p53+/+. (H) The cellular distribution of SNRPA1 protein in HCT116 p53+/+ cells. GAPDH and Lamin B indicate the cytosolic and nuclear fractions, respectively. (I) CRISPR-Cas9–mediated ablation of RMRP reduces the SNRPA1 level in the nucleus, while increases the cytosolic accumulation of SNRPA1, in HCT116 p53+/+ cells. (J) Knockout of RMRP enhances the endogenous interaction of SNRPA1 and HSPA8.