Fig. 5.
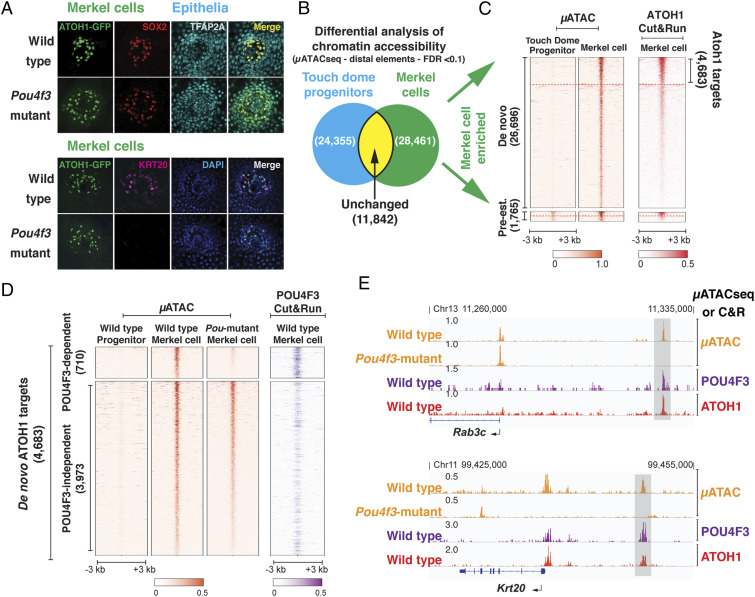
The ATOH1-POU4F3 feed-forward circuit is conserved in Merkel cells. (A). Confocal images of the touch domes from wild-type and Pou4f3-mutant hairy skin. The expression of early Merkel cell markers (ATOH1 and SOX2) in the touch dome is not dependent on Pou4f3 expression. However, the mature Merkel cell marker KRT20 is not expressed in Pou4f3 mutant Merkel cells. (Scale bar, 40 μm.) (B) Venn diagram representing a quantitative comparison of chromatin accessibility at the distal elements between the TDEPs and Merkel cells. A total of 28,461 distal elements are significantly more open in the differentiating Merkel cells (Merkel cell–enriched distal elements), compared to 24,355 distal elements that are more enriched in progenitors. A total of 11,842 distal elements remain unchanged in the two populations (E17.5; FDR < 0.1). (C) Heatmap representation of chromatin accessibility (µATACseq) and ATOH1 binding (C&R) at the 28,461 Merkel cell–enriched distal elements. These elements were separated into pre-established (1,765) and de novo (26,696) clusters. C&R results show ATOH1 targets (4,683) in the de novo cluster (IDR < 0.1). As shown in the hair cells (Fig. 1C), ATOH1 binds to both pre-established and de novo distal elements in Merkel cells. (D) Heatmap representation of the μATACseq results at the 4,683 de novo ATOH1 targets (Left), from wild-type TDEPs, wild-type Merkel cells, and Pou4f3 mutant Merkel cells. Distal elements are clustered into POU4F3 dependent (710) and independent (3,973) based on whether the chromatin accessibility is significantly reduced in Pou4f3 mutant Merkel cells compared to wild-type Merkel cells (FDR < 0.1). POU4F3 C&R from wild-type Merkel cells (Right) indicates direct binding at POU4F3-dependent ATOH1 targets in Merkel cells. (E) Representative genome browser tracks (IGV) of μATACseq and C&R data at two POU4F3-dependent ATOH1 targets in Merkel cells, Rab3c, and Krt20 (Dataset S3).