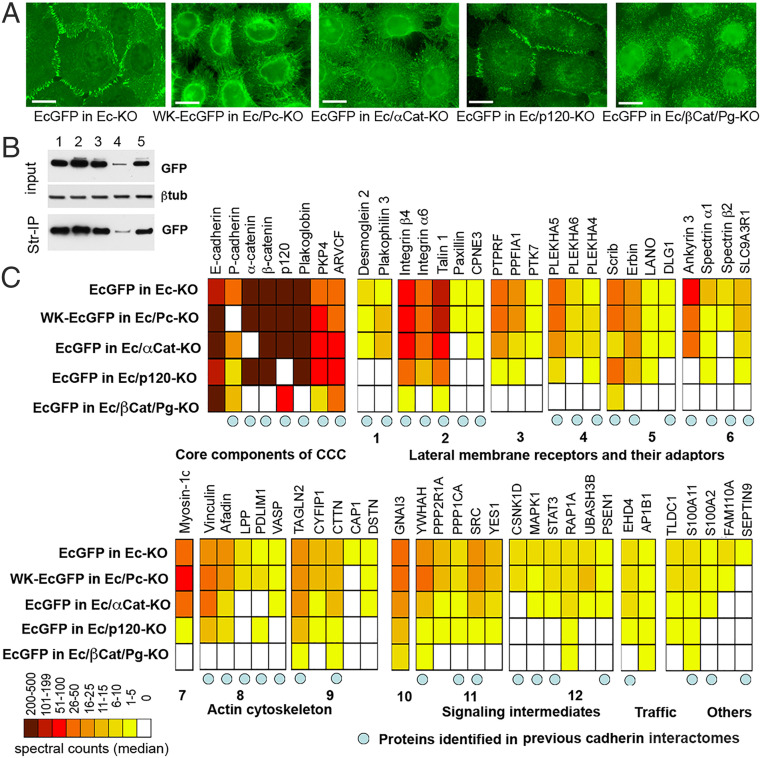
Fig. 1.
Proteins associated with EcGFP and with its adhesion-incompetent mutant WK-EcGFP. (A) Immunofluorescence microscopy of A431 cells expressing GFP-tagged cadherin (EcGFP) or its adhesion-defective mutant (WK-EcGFP) in different genetic backgrounds. EcGFP imaged in the cells with the E-cadherin knockout (EcGFP in Ec-KO); WK-EcGFP imaged in the cells with the combined E- and P-cadherin knockout (WK-EcGFP in Ec/Pc-KO); EcGFP imaged in the cells with the combined E-cadherin and α-catenin knockout (EcGFP in Ec/αCat-KO); EcGFP imaged in the cells with the combined E-cadherin and p120 knockout (EcGFP in Ec/p120-KO); EcGFP imaged in the cells with the combined E-cadherin, β-catenin, and plakoglobin knockout (EcGFP in Ec/βCat/Pg-KO). (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (B) Cell lysates (input) obtained from surface-biotinylated cells shown in A were analyzed for GFP and for the loading control, β-tubulin (βtub). The second parts of the lysates were precipitated using streptavidin agarose (Str-IP) and analyzed for GFP. Note that the p120 knockout, in contrast to other manipulations, results in dramatic reduction of both total and cell-surface E-cadherin levels. (C) Diagram showing the median of spectral counts for each protein identified as associating with cadherin CCCs in our cross-linking experiment. Protein names (or their gene symbols) are given above the diagram, while the genetic backgrounds of the cross-linking experiments are given to the left of the diagram. Proteins are grouped according to their function (given below the diagram). The group of “lateral membrane receptors and adaptors” is further split into components of desmosomes (1), focal adhesions (2), transmembrane phosphatases and their adaptors (3), membrane adaptors of the PLEKHA family (4), polarity regulators (5), and spectrin cytoskeleton (6). The “actin cytoskeleton” is split into actin motors (7), actin-binding proteins (8), and actin dynamic regulators (9). The “signaling components” group includes G protein (10), cortical kinases and phosphatases (11), and intermediates of specific signaling pathways (12). Blue circles indicate proteins previously found in BioID-based classical cadherin interactomes (24–26).