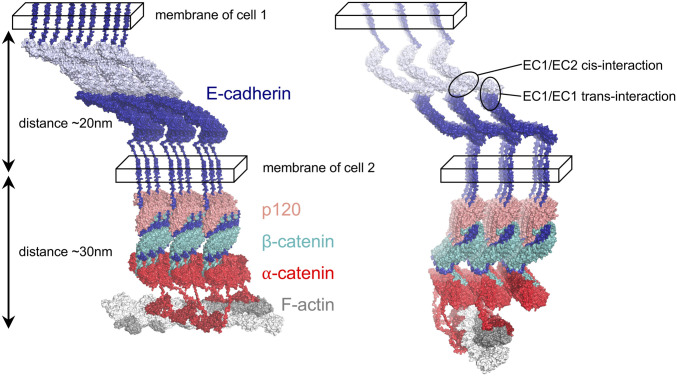
Fig. 4.
Structural model of the E cluster connected to actin. All components of the 3 × 3 lattice, E-cadherin, p120, β-catenin, and α-catenin (color-coded, labeled, and shown in surface representation), satisfy constraints imposed by cis and trans interactions of cadherins (encircled; Right) in the extracellular space (between the two cellular membranes denoted as parallelepipeds). Two views of the lattice are shown. The E cluster is connected to F-actin (shown in gray surface representation) by ABD domains of α-catenin (red) via flexible linkers. F-actin is positioned in such a way that ABD domains from two adjacent rows of CCCs connect to one actin filament by binding the closest available ABD-binding site. The ABD domains (Far Right row of the lattice; dark red) are shown as bound to the rest of α-catenin.