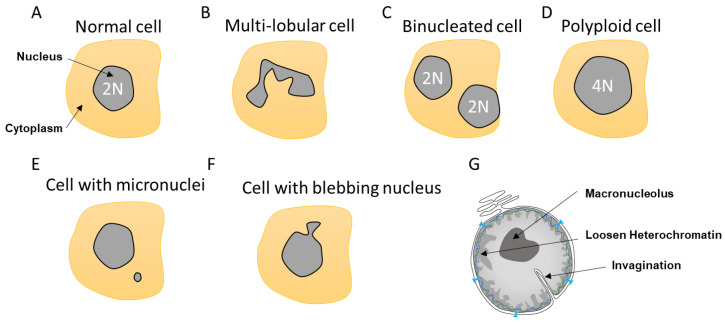
Figure 2.
Different nuclear abnormalities. (A) Classical cells have one single round nucleus that contains a diploid genome (2N). (B) Cells such as neutrophils possess multi-lobar nucleus. (C,D) Polyploid cells (>4N) can either have two or more separated nuclei or one enlarged nucleus. (E) Some cells can have a smaller nucleus, which is called a micronucleus, in their cytoplasm. Micronuclei contain a full chromosome or a piece thereof. (F) Nuclei can also display blebbing characterized by an outward extension of the nuclear envelope (NE). (G). In addition, cancer cells can show abnormalities such as NE invagination, loosen heterochromatin as a consequence in changes in DNA compaction as well as a single and bigger nucleolus, which is called a macronucleolus.