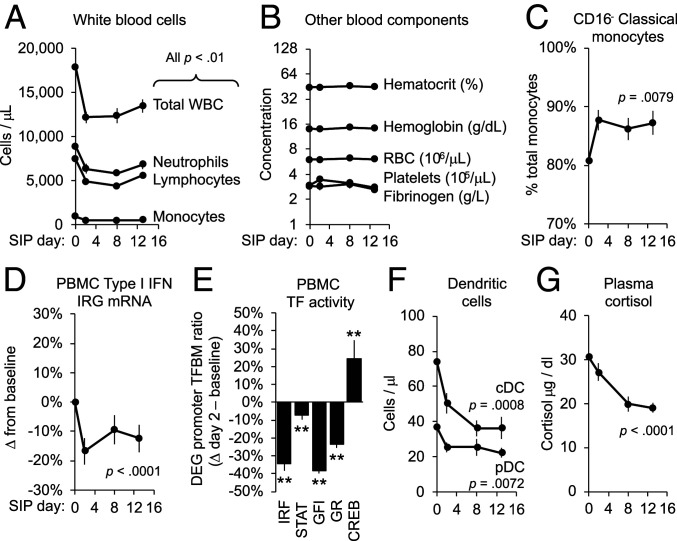
Fig. 1.
Effect of SIP on immune parameters. n = 21 community-housed adult macaques were relocated to individual indoor shelters for 14 d and assessed for (A) major leukocyte subsets, (B) red blood cells and other hematologic parameters, (C) relative prevalence of classical versus nonclassical monocytes, (D) per-cell expression of Type I IFN response genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), (F) classical (cDC) and plasmacytoid (pDC) dendritic cells, and (G) plasma cortisol. (E) Change from baseline to SIP day 2 in bioinformatically inferred activity of IFN-related (IRF, STAT, GFI) and neuroendocrine-related (GR, CREB) transcription factors (TFs). Values: mean ± SE; P values: mixed effect linear model SIP day effect. **P < 0.01 difference from baseline.