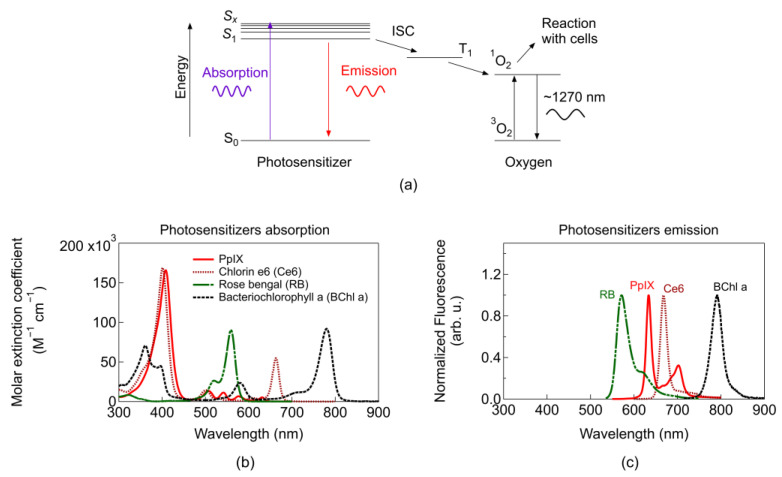
Figure 2.
(a) Simplified Perrin–Jablonski diagram including PDT mechanism of action (ISC: Intersystem crossing). Each arrow indicates an energy conversion process (for simplicity not all possible conversions are depicted). Emission corresponds to the fluorescence of the PS and the 1270 nm emission from the singlet oxygen phosphorescence. (b) Molar extinction coefficient for absorption. (c) Fluorescence emission of typical PSs (data taken from [33,34]). Solvents used for measurements: chloroform for PpIX, toluene for Bacteriochlorophyll a, ethanol for rose bengal and chlorin e6. Additional parameters for common PSs, and PS targeting two-photon absorption can be found in pp. 32–36 in [7], [35], and [21], respectively.