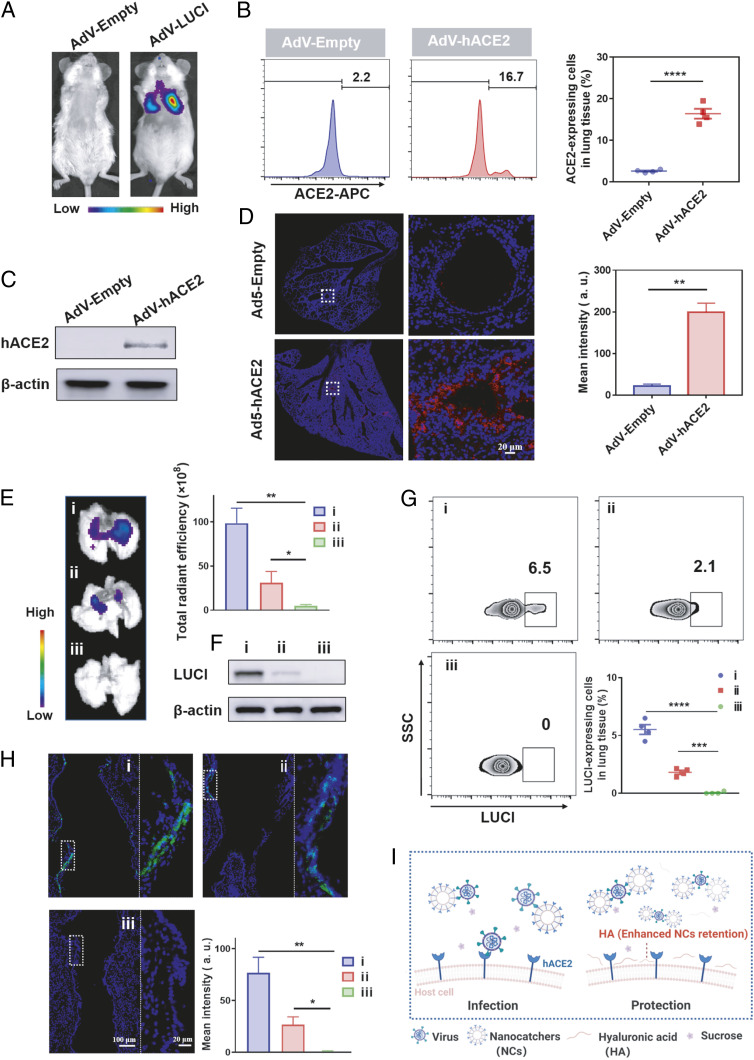
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 infection using the hACE2-expressing mouse model. (A) Bioluminescence image of mice inhaled with LUCI-encoding replication-defective AdV. (B) Representative flow cytometric image (Left) and related quantification results (Right), (C) Western blotting analysis, and (D) immunofluorescence images (Left) and related quantification analysis (Right) of AdV-Empty or AdV-hACE2–transduced lung tissues. (E) Bioluminescence imaging of lungs collected at 48 h post-PBS, NC–sucrose, and NC–HA–sucrose inhalation. (Right) is the quantified intensity of the bioluminescence intensity. (F) Western blotting, (G) flow cytometry, and (H) immunofluorescence analysis of lung tissues collected from mice after different treatments. (i), (ii), and (iii) represent PBS + pseudovirus, NC–sucrose + pseudovirus, and NC–HA–sucrose + pseudovirus group, respectively. (Right) is the enlarged image in (Left) white dotted frame (blue, nuclei; green, LUCI). (I) Scheme indicating the desirable protection effect of NCs against virus infection with the assistance of HA. All data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4). Data are analyzed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.001.