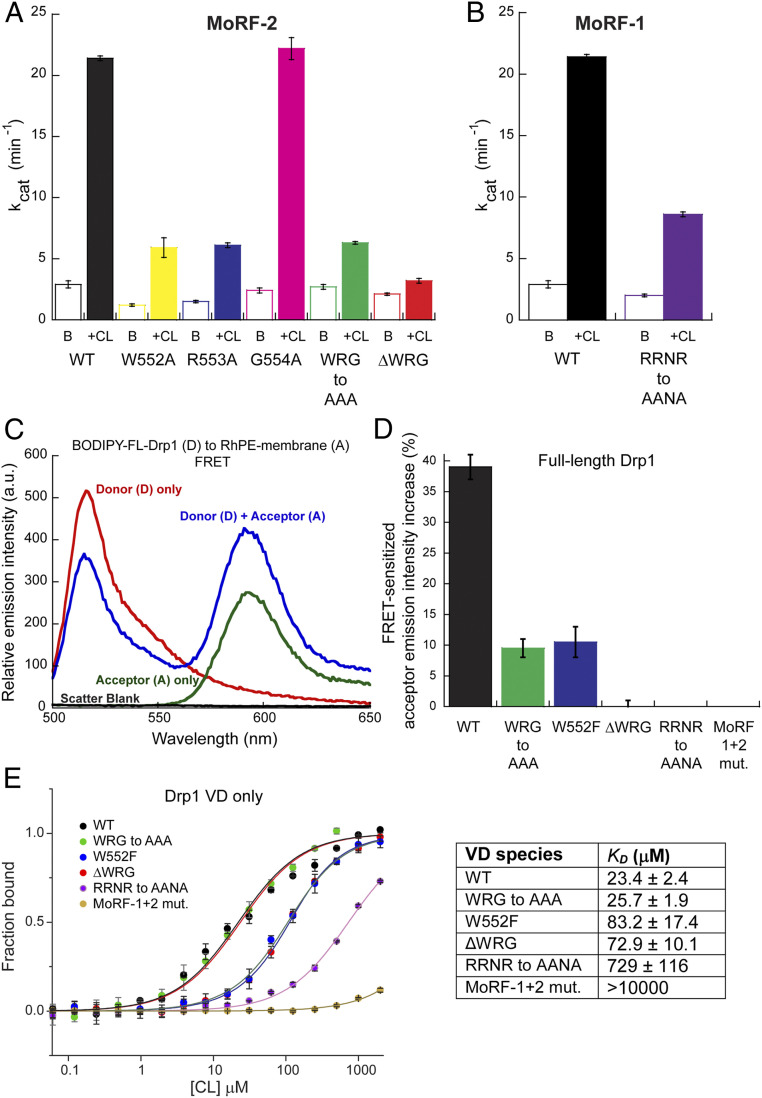
Fig. 4.
MoRF mutations that impair CL interactions. (A and B) Basal (B) and CL-stimulated (+CL) GTPase activities of WT Drp1 in comparison to various MoRF-2 (A) and MoRF-1 (B) mutants. (C) Representative emission spectra of BODIPY-labeled WT Drp1 (donor) in the absence and presence of 1 mol% RhPE (acceptor) in DOPC/DOPE/CL liposomes. FRET was detected by a decrease in donor emission intensity in the presence of acceptor accompanied by a FRET-sensitized increase in acceptor emission upon donor excitation. The A-only trace shows direct excitation of the acceptor at the donor excitation wavelength, which represents the background. Scatter from liposomes was negligible. (D) FRET-sensitized rhodamine emission intensity increase upon incubation of BODIPY-labeled WT Drp1 or mutants with RhPE-labeled, 25 mol% CL-containing liposomes is plotted as a percentage. Data shown are averages ± SEM. (E) MST measurements of WT VD or mutants (0.35 μM final) binding to pure CL (100 mol%) liposomes. Note the logarithmic scale of the x-axis. (Right) The apparent equilibrium dissociation constant or binding affinity (KD) is tabulated. Data shown are averages ± SEM.