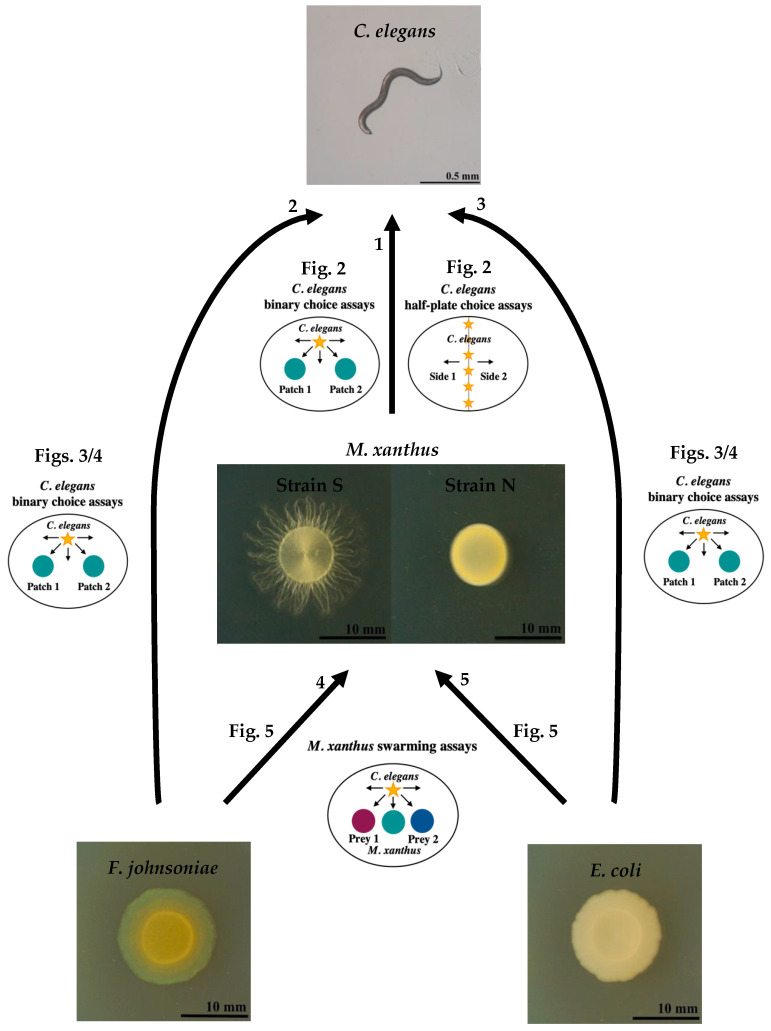
Figure 1.
Predicted trophic interactions of the synthetic community and illustrations of experimental designs. We predicted that C. elegans might function as a potential apex predator in this food web, preying on all other members of the synthetic community (arrows 1, 2, and 3). We predicted M. xanthus to function as a mesopredator that preys upon both basal prey species (arrows 4 and 5) and to experience predation pressure from the nematode apex predator (arrow 1). We show illustrations of the experimental designs that were used to test each depicted interaction and reference the figures that report the relevant results.