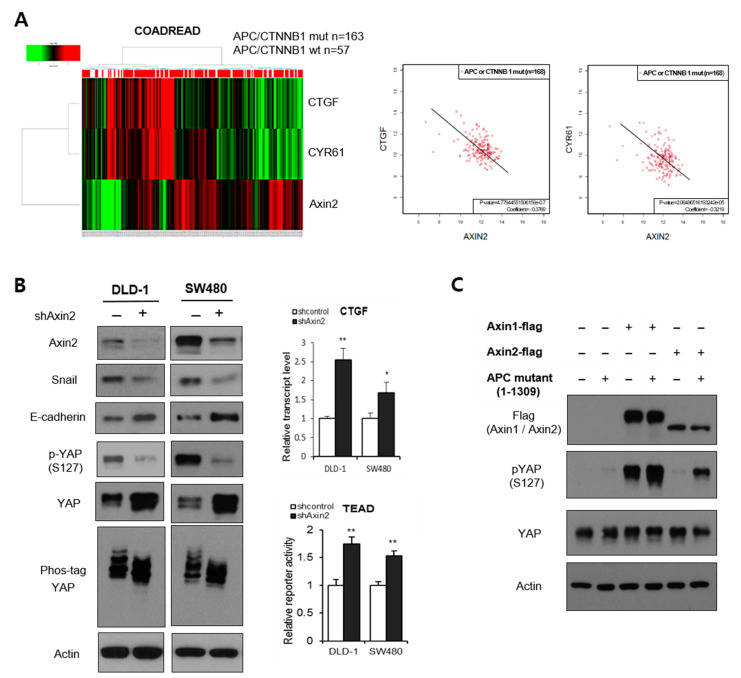
Figure 1.
Axin2 potentiates the Hippo pathway in APC-mutant colorectal cancer. (A) Axin2 transcript abundance in CRC patient samples was inversely correlated to YAP target genes CTGF and CYR61. Those transcript abundances in human COADREAD samples from the TCGA Illumina HiSeq database are represented in a heatmap (left panel, Axin2 vs. CTGF, p = 2.456 × 10−7; Axin2 vs. CYR61, p = 4.068 × 10−6, Pearson correlation). APC or CTNNB1 mutant samples are denoted as red bars. Scatter plots of CTGF, CYR61, and Axin2 transcript in TCGA COADREAD samples having APC or CTNNB1 mutation (n = 168). Axin2 vs. CTGF, R2 = −0.3769, p = 4.779 × 10−7; Axin2 vs. CYR61, R2 = −0.3219, p = 2.0848 × 10−5. (B) Inducible knockdown of Axin2 suppressed Hippo pathway by decreased YAP phosphorylation. YAP phosphorylation level was determined by pS127-YAP antibody and mobility shift on a phos-tag gel in inducible knockdown of Axin2 with doxycycline (Dox) treatment 3 μg/mL for 48 h (left panels). Relative CTGF transcript abundance and TEAD reporter activity of CRC cells expressing inducible shRNA of Axin2 (right). Statistical significances compared to control are denoted as * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 by a two-tailed Student’s t-test. (C) Axin2 increased YAP phosphorylation in the presence of APC mutation. 293 cells were transfected with indicated vectors, and total YAP and phosphorylation YAP (p127-YAP) were determined by Western blot analysis.