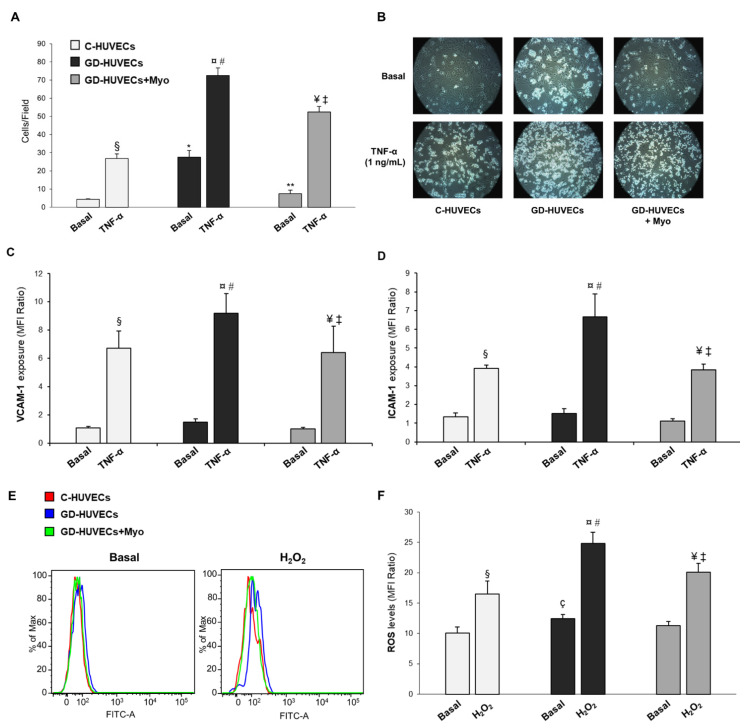
Figure 1.
Effect of supplementing GD mothers with Myo during pregnancy on GD-HUVECs in vitro features. (A) Effect of in vivo treatment with Myo on U937 monocyte adhesion to the endothelium. (B) Representative pictures of C-, GD- and GD+Myo-HUVECs for each experimental condition. (C,D) Effect of in vivo Myo treatment on adhesion molecule membrane exposure (VCAM-1, panel C and ICAM-1, (D). (E) Representative histograms obtained from the cytometric analysis for Basal condition and after H2O2 treatment. (F) Effect of Myo in in vivo treatment on ROS levels in endothelial cells. * p < 0.01 vs. Basal C-HUVECs; ** p < 0.01 vs. Basal GD-HUVECs; § p < 0.05 vs. Basal C-HUVECs; ¤ p < 0.05 vs. Basal GD-HUVECs; ¥ p < 0.05 vs. Basal GD-HUVECs + Myo; # p < 0.05 vs. TNF-α C-HUVECs; ‡ p < 0.05 vs. TNF-α GD-HUVECs; ç p < 0.05 vs. Basal C-HUVECs.