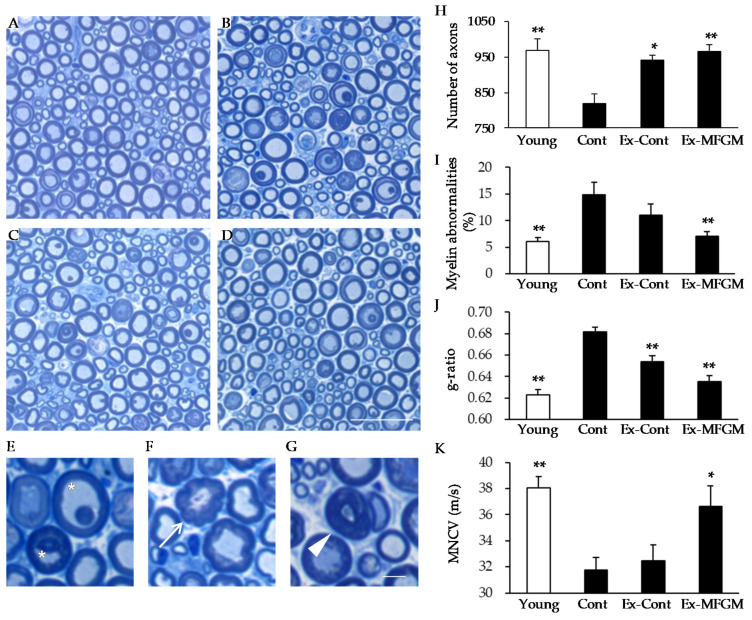
Figure 5.
Effect of MFGM intake with exercise from an old age on nerve structure and function. (A–G) Semi-thin cross-sections of the peroneal nerve stained with toluidine blue. Low-magnification images of nerves at 10 months old (Young; (A)) and 24 months old (Cont, (B); Ex-Cont, (C); Ex-MFGM, (D)) are shown. High-magnification images of nerves are shown in (E–G). Age-related alterations included myelin inclusion (asterisk) (E), myelin outfoldings (arrow) (F), and tomacular structures (arrowhead) (G). (H) Number of axons present in the peroneal nerve. (I) The percentages of myelin abnormalities comprising myelin inclusions, myelin outfoldings, and tomacular structures were determined. (J) The ratio of nerve fiber diameter divided by axon diameter (g-ratio) was calculated. (K) The motor nerve conduction velocity was analyzed. Values are presented as the mean ± SE (n = 5–9 in each group). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. Young group. Scale bars: 30 µm (A–D) and 10 µm (E–G). MFGM, milk fat globule membrane; MNCV, motor nerve conduction velocity; Young, young group; Cont, control diet group; Ex-Cont, control diet with exercise group; Ex-MFGM, milk fat globule membrane diet with exercise group.