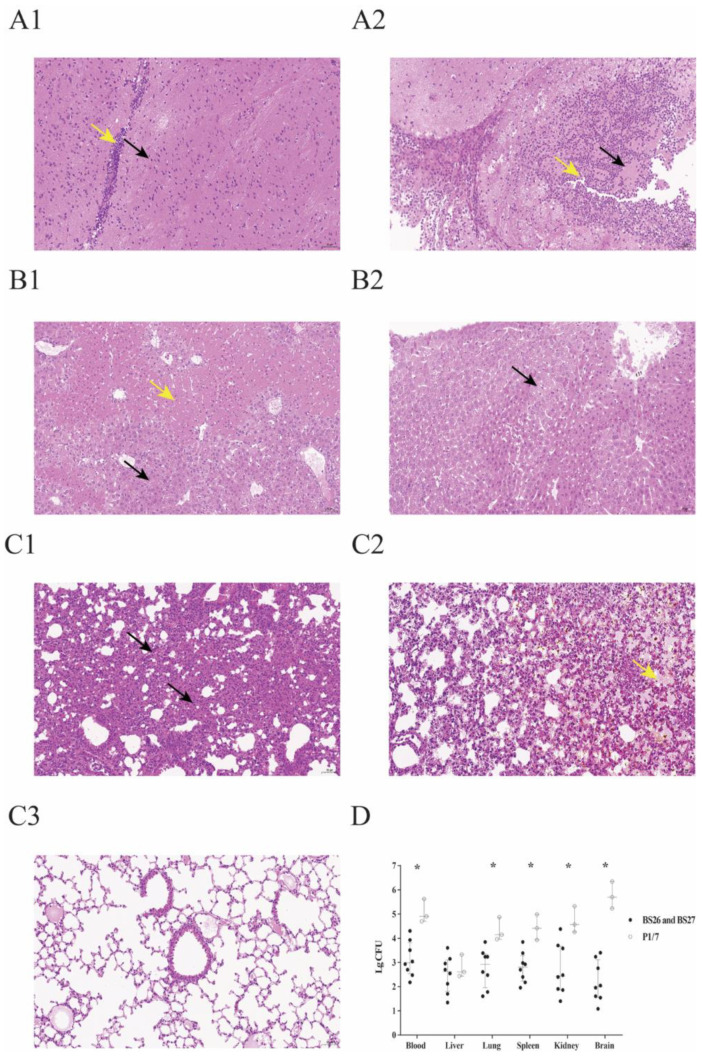
Figure 3.
Histopathological changes and bacterial loads in the organs of survival mice in survival experiment. (A1) Micrograph of brain sample from a S. parasuis strain BS26-infected mouse at 72 h post-infection. Neuronal deformation (black arrowhead) and slight infiltration by lymphocytes (yellow arrowhead) were shown. (A2) Micrograph of brain sample from a mouse infected with S. suis strain P1/7 at 72 h post-infection. Neuronal necrolysis (black arrowhead) and significant infiltration by neutrophils (yellow arrowhead) were shown. (B1) Micrograph of liver sample from a mouse infected with S. parasuis strain BS26 at 72 h post-infection. Hepatocyte steatosis (black arrowhead) and coagulative necrosis (yellow arrowhead) were shown. (B2) Micrograph of liver sample from a mouse infected with S. suis strain P1/7 at 72 h post-infection. Edema of few hepatocytes was shown (black arrowhead). (C1) Micrograph of lung sample from a mouse infected with S. parasuis strain BS26 at 72 h post-infection. Alveoli wall thickening with diffused infiltration of neutrophils and lymphocytes (black arrowhead) was shown. (C2) Micrograph of lung sample from a mouse infected with S. parasuis strain BS26 at 72 h post-infection. Hemorrhagic foci (yellow arrowhead) are shown. (C3) Micrograph of lung sample from a mouse infected with S. suis strain P1/7 at 72 h post-infection. No significant histopathological lesions were observed. H&E staining, ×200 magnification, scale: 50 μm. (D) Bacterial loads in blood and organs of survival mice. Colonies were expressed as CFU/0.1 g for organ samples or CFU/mL for blood samples. Bacterial counts of individuals, including median with interquartile ranges, are presented. Significant difference in bacterial counts between S. suis and S. parasuis-infected groups was determined by Wilcoxon’s two-sample test. *, significantly different (p < 0.05) in bacterial counts between S. suis strain P1/7-infected group and S. parasuis strains-infected group.