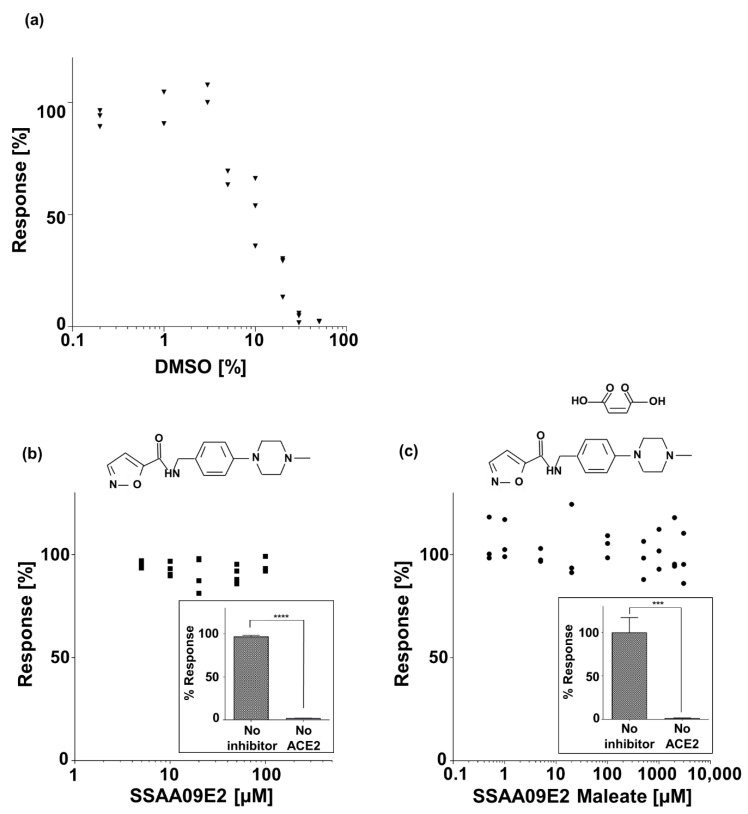
Figure 5.
Assessing a small molecule (SSAA09E2) as an inhibitor of the S1-ACE2 interaction. In each binding curve, the signals were normalized to the signal at 0 µM of inhibitor, which was set as 100% Response. (a) A binding curve of S1-ACE2 interaction with increasing concentrations of DMSO. The experiment was repeated three times (. (b) A binding curve of S1-ACE2 interaction with increasing concentrations of SSAA09E2 in a final concentration of 1% v/v DMSO. The experiment was repeated three times (). (Inset) Abbreviations: “No inhibitor”, conjugated magnetic beads with the attached S1 protein were incubated with biotinylated ACE2 protein and SA-PE. “No ACE2”, conjugated magnetic beads with the attached S1 protein were incubated with the inhibitor and SA-PE, but without the ACE2 protein. Measurements were normalized to the signal (designated as 100% Response) when S1 binds with ACE2 without an inhibitor and without DMSO. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean value of four experiments (. Four asterisks (****) indicate a statistical significance of . (c) A binding curve of S1-ACE2 interaction with increasing concentrations of SSAA09E2 Maleate dissolved in DDW. The experiment was repeated three times (). (Inset) Abbreviations: “No inhibitor”, conjugated magnetic beads with the attached S1 protein were incubated with biotinylated ACE2 protein and SA-PE. “No ACE2”, conjugated magnetic beads with the attached S1 protein were incubated with the inhibitor and SA-PE, but without the ACE2 protein. Measurements were normalized to the average signal (designated as 100% Response) when S1 binds with ACE2 without an inhibitor. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean value of five experiments (. Three asterisks (***) indicate a statistical significance of .