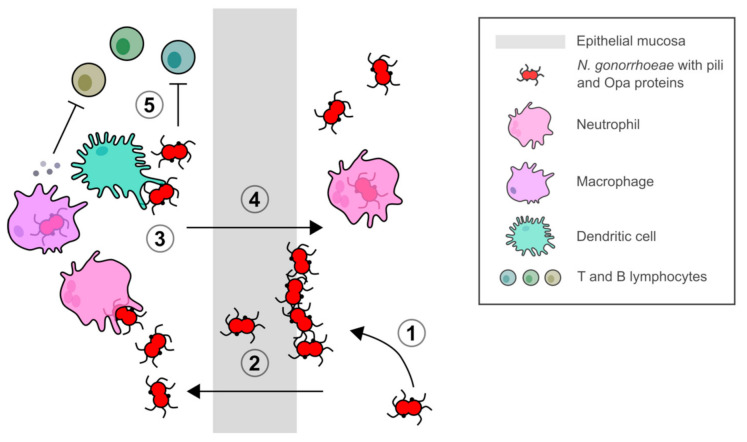
Figure 2.
N. gonorrhoeae infection, transmission, and modulation of host immunity. (1) Attachment and colonization of N. gonorrhoeae mediated by Type IV pili and Opa proteins. (2) Colonization and invasion of host epithelium and transcytosis through epithelial mucosa. (3) Stimulation of local mucosal immune cells and host inflammatory response. (4) Transmission of bacteria in a neutrophil-rich exudate. (5) Modulation of immune response of T and B lymphocytes by stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines by phagocytic cells to enhance a Th17 immune response and suppress Th1/2 immune responses.