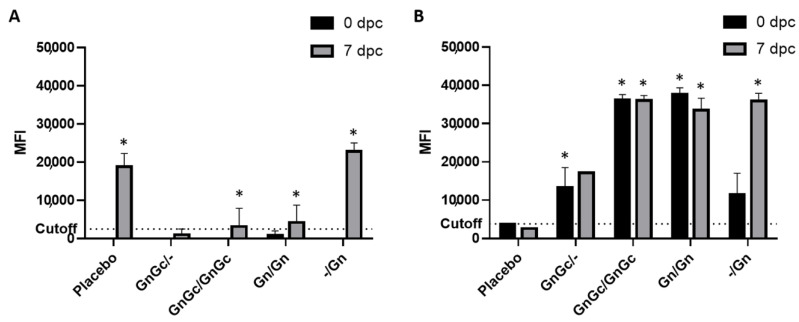
Figure 3.
RVFV Fluorescence Microsphere Immunoassay FMIA enables differentiation of infected from vaccinated (DIVA) cattle using (A) RVFV N and (B) Gn recombinant proteins. FMIA was used to further evaluate the efficacy of candidate RVFV subunit vaccines to induce antigen-specific antibodies. The cattle were vaccinated with the respective subunit vaccine formulations and at 35 days post initial vaccination were challenged with the RVFV Ken06 strain and maintained for up to 10 days post challenge (dpc). The detection of IgG antibodies in sera against the N and the Gn target proteins at 0 and 7 dpc are shown, and reported as median fluorescence intensity (MFI). Assay cutoff is at 2500 MFI for the N target and 3800 MFI for the Gn target. RVFV N served as the DIVA-compatible marker. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test for adjusted p values using Graph Pad Prism software. (A) At 7 dpc, GnGc/GnGc, GnGc/- and Gn/Gn groups were significantly different (* p value < 0.001) compared to the placebo and -/Gn groups. (B) At 0 dpc, GnGc/GnGc and Gn/Gn groups were significantly different (* p value < 0.0001) compared to the placebo, GnGc/- and -/Gn groups and GnGc/- groups were significantly different (* p value < 0.05) compared to placebo; at 7 dpc, GnGc/GnGc, Gn/Gn and -/Gn groups were significantly different (* p value < 0.0001) compared to the placebo, and the GnGc/GnGc group versus the GnGc/- group; also the GnGc/- group was significantly different (* p value < 0.001) compared to the Gn/Gn and -/Gn groups.