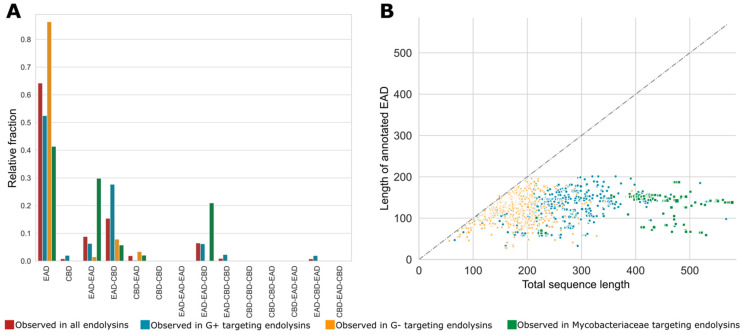
Figure 5.
Relative fractions of specific single, bi- and tri-modular architectures for endolysins with different host specificities and the putative presence of unannotated domains. (A) The relative occurrence of each of the theoretically possible single, bi- and trimodular architecture comprising EADs and CBDs is set out for all unique endolysin sequences (red) and split up for endolysins from phages infecting Gram-positive bacteria (blue), Gram-negative bacteria (yellow) and Mycobacteriaceae (green). These fractions sum to one for each group of hosts; (B) the length of the annotated domain versus the total sequence length of EAD-only architectures. To accommodate for the variable numbers of repeats of a single CBD, they were condensed into a single occurrence of the domain. This analysis shows that mainly endolysins targeting Gram-positive and Mycobacteriaceae hosts comprise unannotated domains.