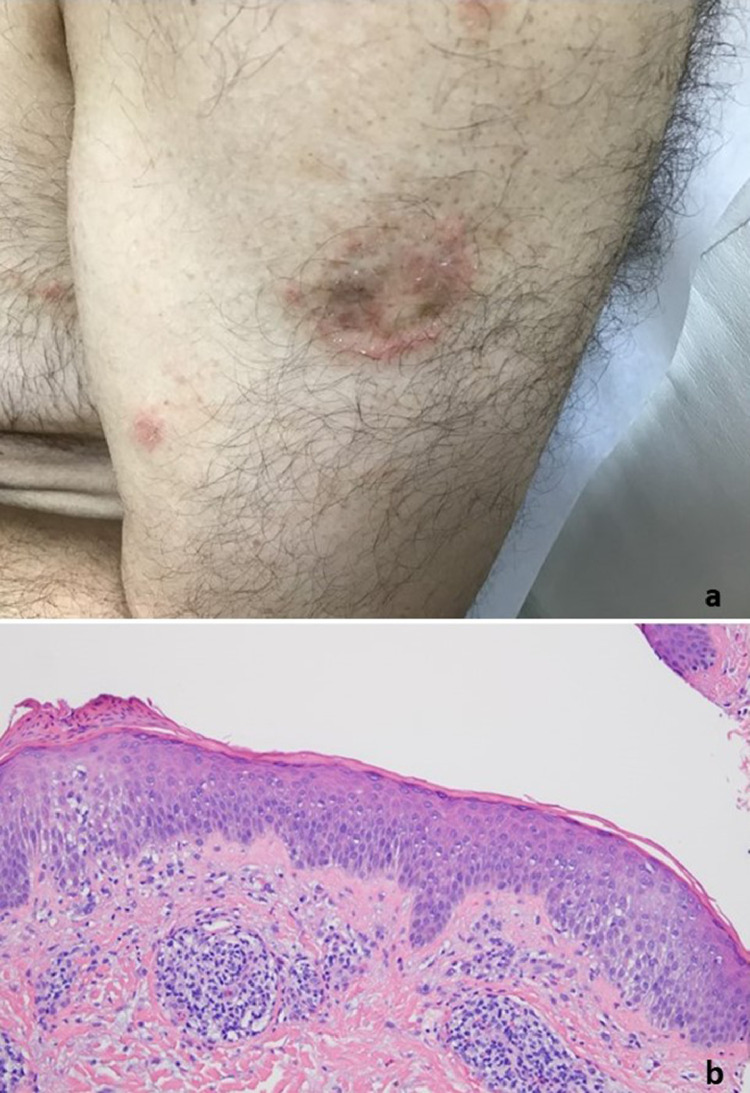
Fig. 7.
T-cell response with features of an eczematous dermatitis (case 19). The patient developed an eczematous reaction almost immediately after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine. (A) Nummular plaques involved 20% of the body (reproduced with permission from Dr. Scott Sanders, New City, NY). The biopsy showed an eczematous dermatitis characterized by acanthosis, intercellular edema, and exocytosis of lymphocytes and monocytes into the epidermis. (B) A subtle cell-poor–interface dermatitis is also observed. A lymphocytic purpuric vascular reaction is also noted (hematoxylin and eosin, 200 ×). COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019.