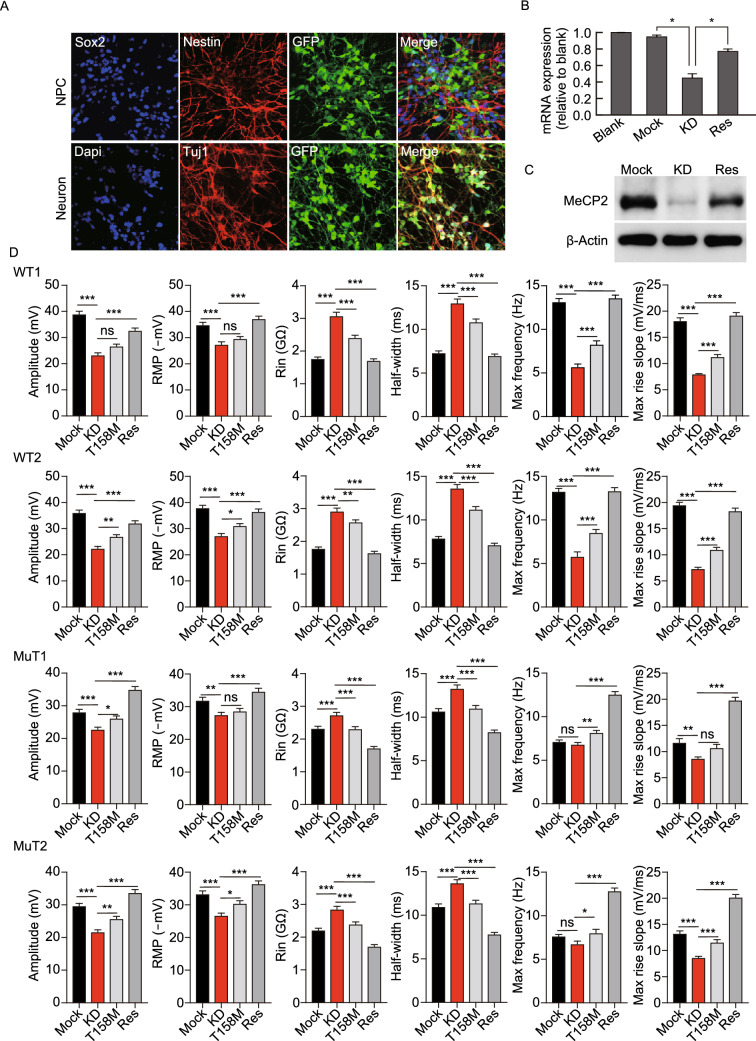
Figure 4.
Causal relationship between MeCP2-deficiency and AP phenotypes: KD and rescue experiments. (A) Representative images of lentivirus infected hiPSC-derived NPCs, expressing Sox2 and Nestin, and neurons, expressing Tuj1, indicating continued expression of lentivirus-driven GFP during neuronal differentiation. Three types of lentivirus were used: Mock, empty lentivirus; KD, shRNA driven KD of endogenous MeCP2; Res, KD of endogenous MeCP2 and expression of exogenous shRNA resistant WT MeCP2. Every whole-cell recordings were performed on GFP labeled neurons (Bar: 25 μm). (B) MeCP2 mRNA expression assessed by qPCR in non-infected NPCs (blank) and NPCs infected with Mock, KD or rescue lentivirus. Infection with Mock lentivirus does not affect MeCP2 mRNA expression, whereas KD lentivirus reduces MeCP2 expression. Rescue lentivirus stores MeCP2 mRNA level back to normal. n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05. (C) MeCP2 protein expression assessed by WB performed on infected NPCs showing KD of MeCP2 after infection with KD virus (KD), while rescue virus (Res) restores MeCP2 expression to a level close to WT control. (D) Electrophysiological properties of WT, R106W-MuT subjected to Mock, MeCP2-KD, MeCP2-T158M-Rescue and MeCP2-WT-Rescue. n (WT1-Mock) = 14 neurons; n (WT2-Mock) = 15 neurons; n (MuT1-Mock) = 13 neurons; n (MuT2-Mock) = 14 neurons; n (WT1-KD) = 8 neurons; n (WT2-KD) = 10 neurons; n (MuT1-KD) = 12 neurons; n (MuT2-KD) = 13 neurons; n (WT1-T158M) = 14 neurons; n (WT2-T158M) = 15 neurons; n (MuT1- T158M) = 14 neurons; n (MuT2-T158M) = 13 neurons; n (WT1-Res) = 15 neurons; n (WT2-Res)=14 neurons; n (MuT1-Res) = 15 neurons; n (MuT2-Res) = 16 neurons. Error bars stand for standard error. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001