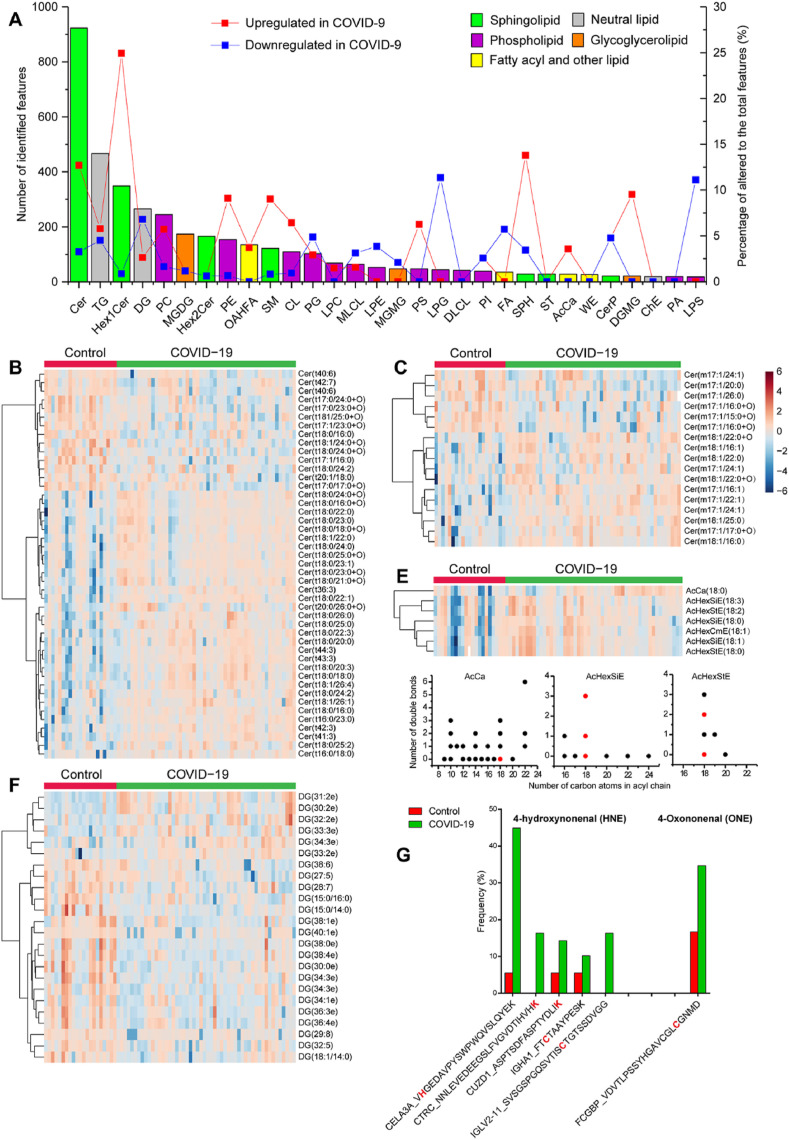
Fig. 6.
Fecal lipidome alterations in COVID-19 patients. A. Distribution of top 30 lipid subclasses identified in untargeted fecal lipidomics. The bar plots indicate number of all identified lipids (left y-axis) and the solid line correspond to the proportion of altered lipids (right y-axis) within each subclass. B-E. Heatmap depicting the relative abundance of differentially expressed lipid subclasses (Wilcoxon's rank sum test, q < 0.05) in COVID-19. Several lipid subclasses exhibited chain-length dependent alterations including ceramide (Cer) lipids with trihydroxy (B) or monohydroxy (C) sphingoid bases, as well as fatty acyl lipids and neutral lipids (D and F). F. Distribution of chain length and number of double bonds of upregulated (red dots) and unchanged (black dots) fatty acyl lipids and neutral lipids (no downregulated feature was observed). Degree-of-unsaturation dependent alterations were observed in Cer with trihydroxy bases (B) and DG lipids (E). G. Increased frequency of protein modification by lipid peroxidation products 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) and 4-oxononenal (ONE). The identifier of features is presented using the format: gene name_peptide sequence (the modification sites are highlighted in red). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)