Figure 2.
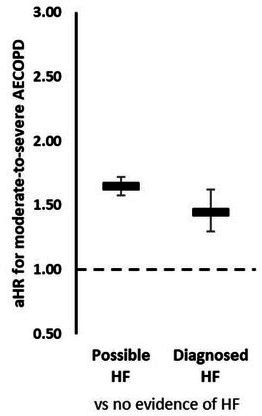
Effect of newly diagnosed and possible HF on AECOPD risk. aHR comparing risk of moderate-to-severe AECOPD in patients with COPD with possible HF and newly diagnosed HF compared with patients with COPD without evidence of HF. Estimates from stratified Cox regression stratified by matched set (sex and age) and adjusted for smoking status, body mass index, index of multiple deprivation, exacerbation history, severity of airflow limitation, inhaler use, a history of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular medication use. AECOPD, acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; aHR, adjusted HR; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; HF, heart failure.
