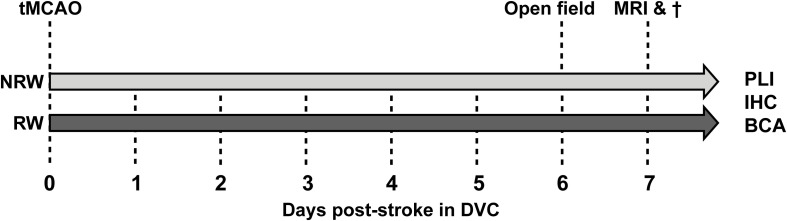
FIGURE 1.
After right transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO), mice were randomly allocated into a running wheel (RW) group and a no running wheel (NRW) group. RW mice had 24/7 access to voluntary exercise, while control mice had no running wheel in the cage. Activity/walking patterns of each mouse was individually monitored in digital ventilated cages (DVC) 24/7 for 1 week. Moreover, an open field test was performed to further investigate locomotion and activity. Immediately after MRI scanning, animals were sacrificed and brains were obtained to perform post-mortem immunohistochemistry (IHC), biochemical analysis (BCA), and polarized light imaging (PLI).