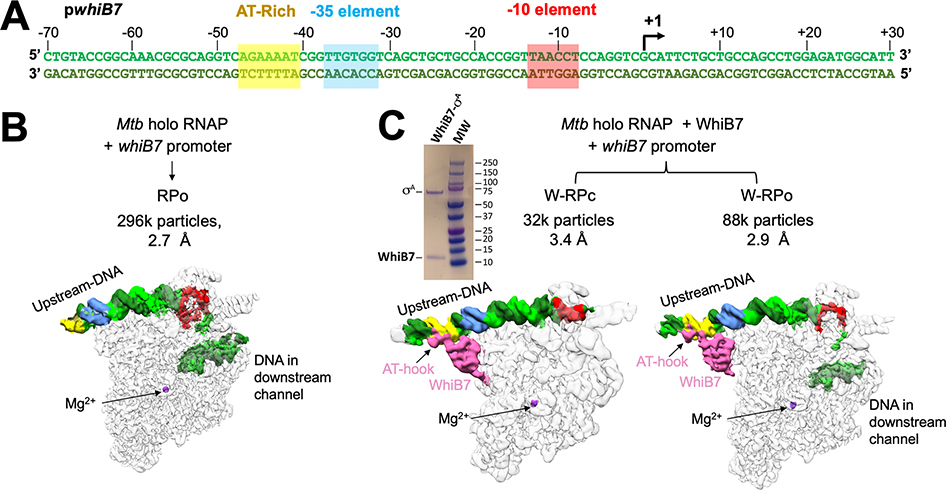
Figure 1. Cryo-EM analysis of Mtb RNAP initiation complexes on the whiB7 promoter reveal distinct transcription intermediates.
A. Duplex Mtb whiB7 promoter fragment used for cryo-EM. The promoter elements (AT-rich WhiB7 regulatory motif; yellow, −35 element, blue; −10 element, red) and the transcription start site (+1; arrow) are denoted. The top (non-template) strand and bottom (template) strand are colored light and dark green, respectively.
B. Structural class derived from the cryo-EM data without WhiB7 on the whiB7 promoter. Cryo-EM composite maps are low-pass filtered according to the local resolution (Figure S2I) (Cardone et al., 2013) and shown as white transparent molecular surfaces. The DNA is shown as a solid surface and colored as in (A). The active site Mg2+ is indicated for reference. The number of particles and nominal resolution of each structure are indicated above the structures.
C. Structural classes derived from the cryo-EM data and with WhiB7 on the whiB7 promoter. Cryo-EM composite maps are low-pass filtered according to the local resolution (Figures S2C, F) (Cardone et al., 2013) and shown as white transparent molecular surfaces. The DNA is shown as a solid surface and colored as in (A). WhiB7 is colored in pink and the active site Mg2+ is indicated for reference. The number of particles and nominal resolution of each structure are indicated above the structures. Upper left, Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE analysis of purified σA/WhiB7 complex.