Figure 4. Increased AEA signalling at TRPV1Rs augmented freezing behaviour at extinction training and retrieval in females.
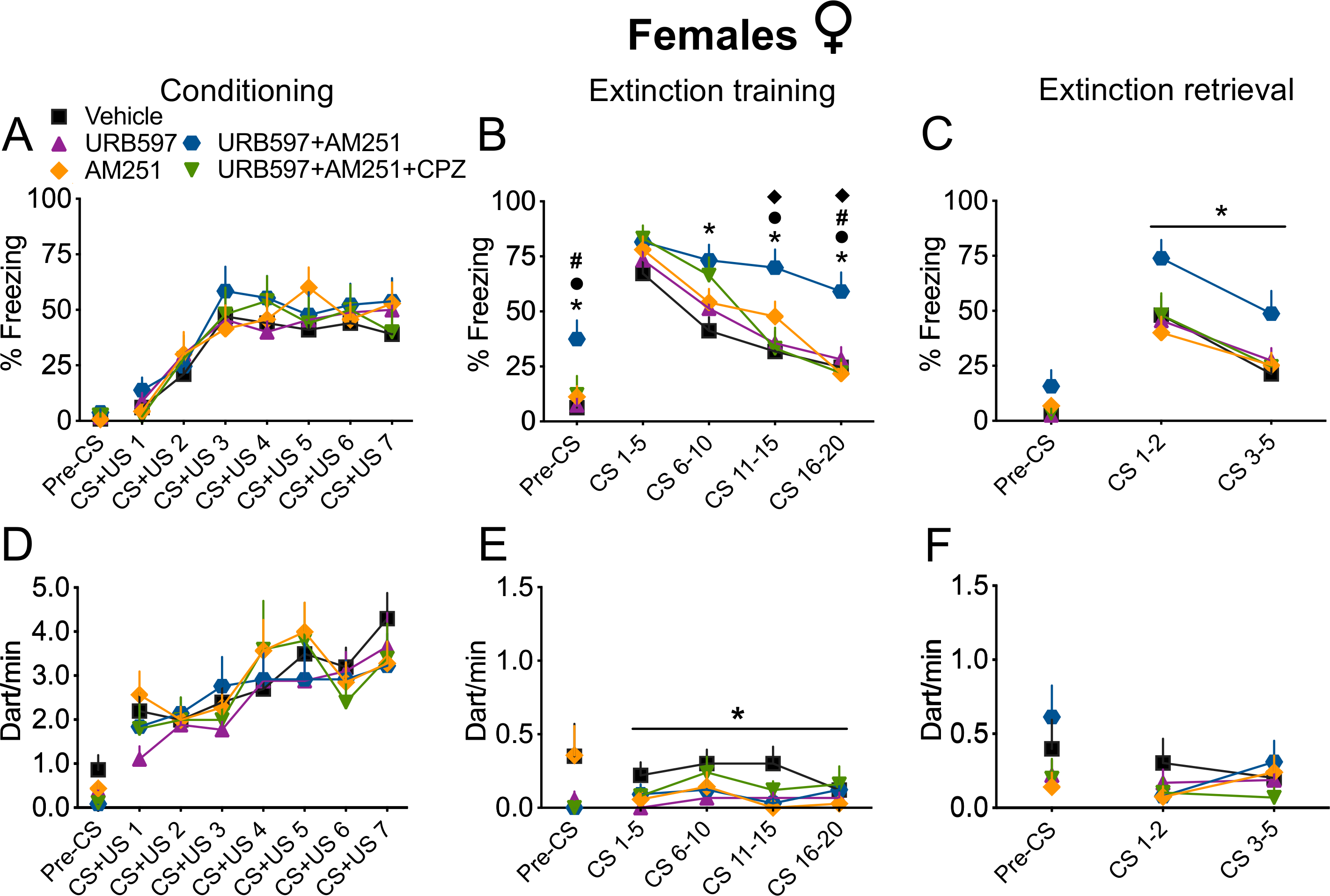
(A-F) Treatment with the AEA hydrolysis inhibitor URB597 with concurrent blockade of CB1R with the antagonist AM251 (URB597+AM251) induced fear generalization, impaired within-session extinction and extinction retrieval. These effects were mediated by AEA signalling at TRPV1Rs, as they were completely blocked by concomitant injection with the TRPV1R antagonist CPZ (URB597+AM251+CPZ). Furthermore, treatment with URB597 alone induced an overall reduction of darting behaviour during CS presentation at extinction training compared to the vehicle group. Percentage of freezing during auditory fear conditioning (A), extinction training (B) and extinction retrieval (C). Number of darting events/min (dart/min) during auditory fear conditioning (D), extinction training (E) and extinction retrieval (F). Vehicle, n = 20; URB597, n = 18; AM251, n = 14; URB597+AM251, n = 13; URB597+AM251+CPZ, n = 10. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05 vs Vehicle; • P < 0.05 vs URB597; # P < 0.05 vs AM251; ◆ P < 0.05 vs URB597+AM251+CPZ. Horizontal line below the star indicates a main effect of drug: P < 0.05, URB597+AM251 group vs Vehicle group (C) and URB597 group vs Vehicle group (E).
