Table 2.
Strategies in the design of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines that use RBD of the S glycoprotein.
| Developers | Vaccine | Vaccine platform | Phase | Design of vaccines using RBD as antigen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention | DelNS1-2019-nCoV-RBD-OPT1 | VVr | Phase 2 |

|
| West China Hospital + Sichuan University | Recombinant (Sf9 cell) | PS | Phase 2 |

|
| Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine | ND | PS | ND |

|
| United Biomedical + COVAXX | UB-612 | PS | Phase 1 |
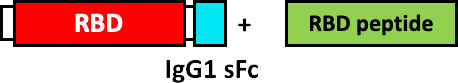
|
| Kentucky BioProcessing | KBP-COVID-19 | VLP | Phase 2 |
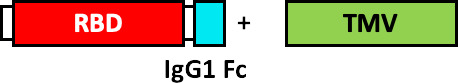
|
| AdaptVac (PREVENT-nCoV) | ND | VLP | ND |
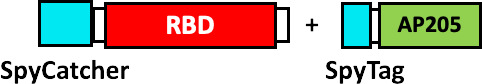
|
| Anhui Zhifei Longcom Biopharmaceutical + Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences | RBD-Dimer | PS | Phase 3 |

|
| Pfizer/BioNTech | BNT162b1 | RNA | Phase 3 |

|
| Cansino Biologics | ND | – | ND |
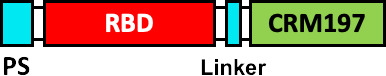
|
| Sun Yat-sen University | ND | VLP | ND |
|
Envelope Glycoprotein Signal Sequence from Baculovirus GP67 (GP67 ss), crystallizable fragment of IgG1 (IgG1 Fc), Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), coat protein of Acinetobacter phage AP205 (AP205), non-toxic mutant of diphtheria toxin (CRM197), SpyCatcher (SC), SpyTag (ST) and secretory signal peptide (SP).
