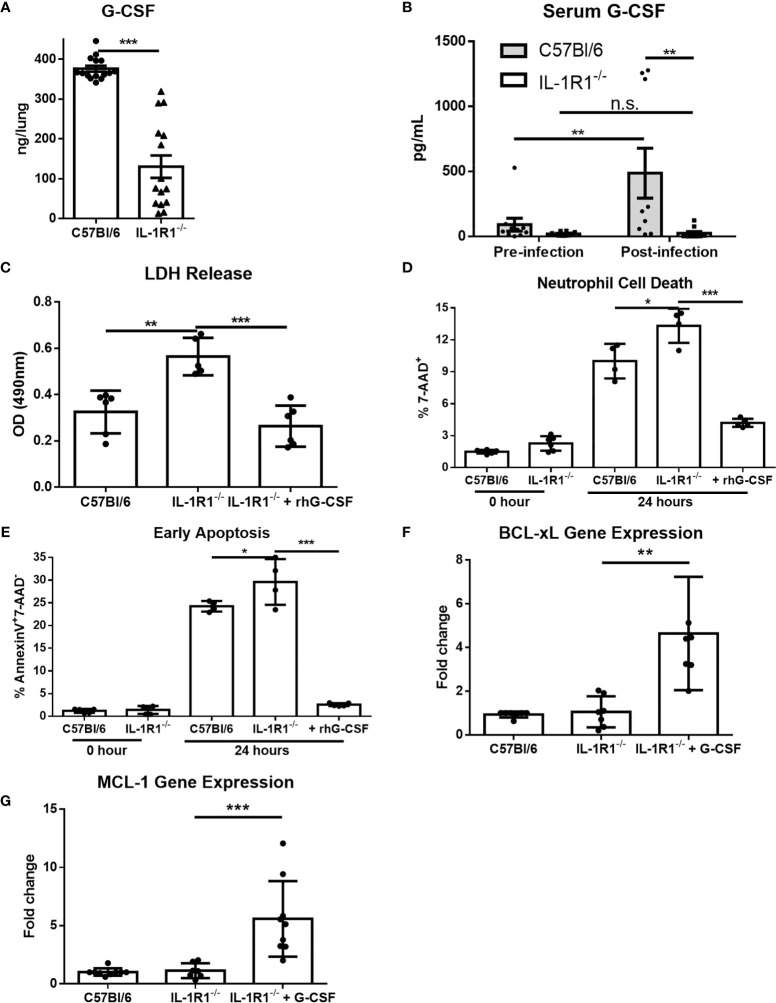
Figure 8.
G-CSF secretion is IL-1 receptor-dependent, and reduces neutrophil cell death and increases anti-apoptotic gene expression. (A) Pulmonary G-CSF production in lungs of the indicated mouse strains infected for 3 days with A. fumigatus beads. Results represent the mean ± SEM of groups of at least 16 mice across 2 experiments, ***p ≤ 0.001, (Student’s t-test). (B) G-CSF quantified from the serum of the indicated strains of mice before and 3 days after infection with A. fumigatus. Results represent the mean ± SEM of groups of at least 10 mice, **p ≤ 0.01, (two-way ANOVA). (C) Neutrophil cell death from bone marrow isolated neutrophils of the indicated strains as measured by LDH release with or without 24 hours incubation with 600ng/mL of G-CSF as indicated. Results represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments, **p ≤ 0.001 and ***p ≤ 0.001, (one-way ANOVA test). (D) Neutrophil cell death as measured by 7-AAD staining and flow cytometry analysis directly after isolation (0 Hour) or after 24 hours of culture in 10% FBS supplemented RPMI. Cultures were supplemented with 600ng/mL of G-CSF where indicated. Results represent means ± SD of 2 independent experiments, *p ≤ 0.05, (one-way ANOVA test). (E) Neutrophil apoptosis as measured by Annexin V staining either directly after isolation (0 hour) or after 24 hours of culture with or without supplementation with 600ng/mL of G-CSF. Results represent mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments, **p ≤ 0.01, (one-way ANOVA test). (F, G) Fold change in gene expression of anti-apoptotic genes BCL-xL and MCL-1 as measured by qPCR from bone marrow isolated neutrophils after 24 hours of culture. IL-1R1-/- neutrophils were also treated with 600ng/mL of G-CSF. Results represent mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments, **p ≤ 0.01, (one-way ANOVA test).