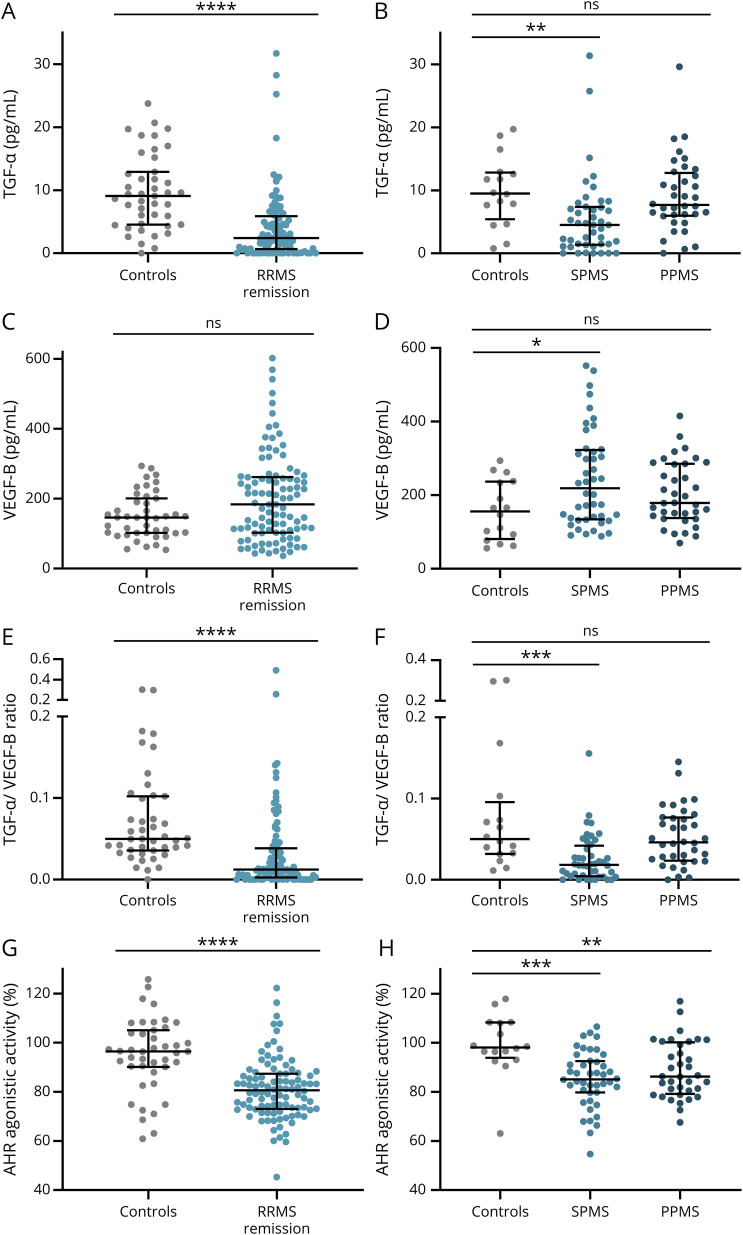
Figure 1. TGF-α/VEGF-B Ratio and AHR Agonistic Activity Are Decreased in Patients With MS.
TGF-α (A, B) and VEGF-B (C, D) levels as well as AHR agonistic activity (G, H) in serum samples of patients with RRMS in remission (n = 98), SPMS (n = 44), PPMS (n = 36), and their respective controls (A, C, E, G: n = 43; B, D, F, H: n = 16) were assessed. TGF-α and VEGF-B levels were measured in pg/mL using a human TGF-α or VEGF-B ELISA. TGF-α/VEGF-B ratio (E, F) was determined by dividing TGF-α levels by VEGF-B levels. An AHR ligand–sensitive luciferase assay was used. Relative activity was calculated by dividing firefly luciferase activity (pGud-Luc) by Renilla luciferase activity (pTK-Renilla). Values are means of duplicate measurements. Lines represent median and interquartile range. Significance levels were derived using nonparametric tests (Mann-Whitney test and Kruskal-Wallis test with the Dunn multiple comparison test correcting for multiple comparisons). ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.001, *p < 0.01, and ns = nonsignificant. AHR = aryl hydrocarbon receptor; MS = multiple sclerosis; PPMS = primary progressive MS; RRMS = relapsing-remitting MS; SPMS = secondary progressive MS; TGF-α = transforming growth factor alpha; VEGF-B = vascular endothelial growth factor B.