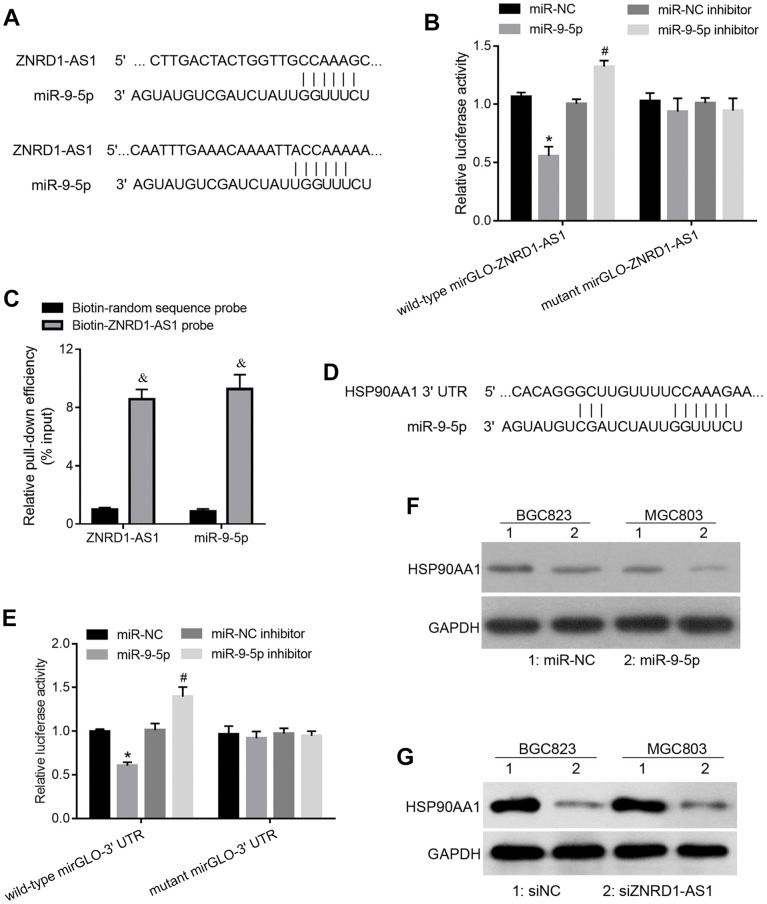
Figure 3.
ZNRD1-AS1 targets the miR-9-5p/HSP90AA1 axis. (A) miR-9-5p binding site in the ZNRD1-AS1 sequence. (B) Relative luciferase activity of recombinant luciferase reporter wild-type mirGLO-ZNRD1-AS1 and mutant mirGLO-ZNRD1-AS1 in human embryonic kidney 293T cells cotransfected with miR-NC, miR-9-5p mimic, miR-NC inhibitor, or miR-9-5p inhibitor. (C) Relative ZNRD1-AS1 and miR-9-5p levels in RNA enriched by pulldowns. After transfection with biotinylated ZNRD1-AS1 probe (50 μM) or random sequence probe (50 μM) for 24 h, BGC823 cells were harvested for the pull-down assay. (D) miR-9-5p binding site on 3’ UTR of HSP90AA1. (E) Relative luciferase activities of recombinant luciferase reporter wild-type mirGLO-3’ UTR and mutant mirGLO-3’ UTR when cotransfected with miR-NC, miR-9-5p mimic, miR-NC inhibitor, or miR-9-5p inhibitor. (F) Protein expression of HSP90AA1 in MGC803 and BGC823 cells transfected with siZNRD1-AS1 or siNC, as detected by western blotting. (G) Protein expression of HSP90AA1 in MGC803 and BGC823 cells transfected with siZNRD1-AS1 or siNC, detected by western blotting. *p <0.05, for miR-9-5p vs. miR-NC; #p <0.05, for miR-9-5p inhibitor vs. miR-NC inhibitor; &p <0.05, for biotin-ZNRD1-AS1 probe vs. biotin-random sequence control probe.