Fig. 1.
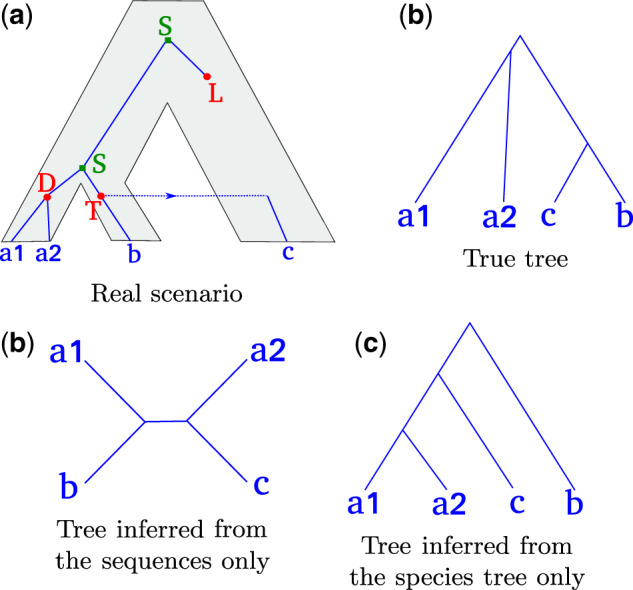
A gene tree evolving along the species tree, and several possible inferred trees. (a) The true history. The gene tree (blue lines) evolves within the species tree (gray area) and undergoes speciations (S), duplications (D), losses (L), and HGT (T). (b) The true rooted gene tree. (c) An unrooted gene tree inferred with a sequence-aware method. The splits between gene lineages are very close in time, and there is not enough signal in the sequences to correctly infer the unrooted gene tree topology. (d) Rooted tree inferred from the species tree only (without accounting for the sequences), assuming that HGTs are less likely than duplications
